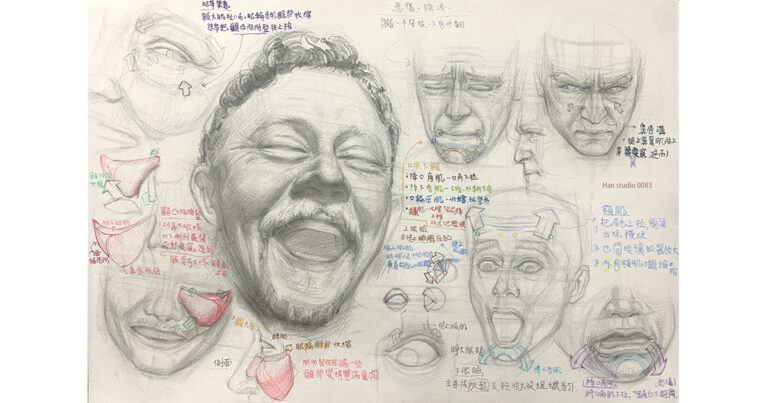
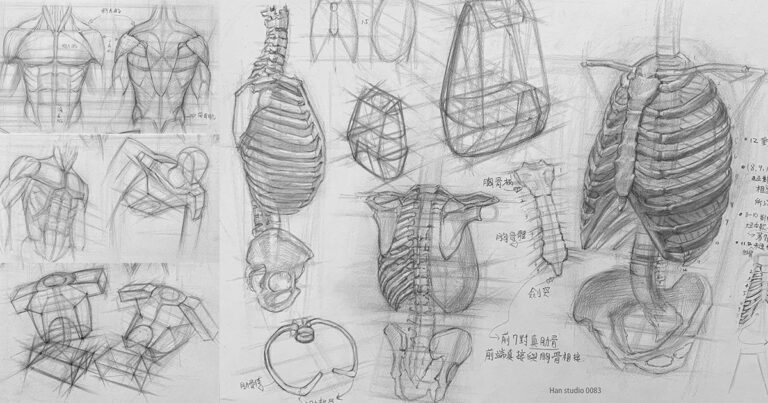
Record of This Week’s Watercolor Practice: Exploring Variations Between Different Containers 🙋
In a recent workshop at our studio, we invited a guest speaker who impressed us by performing a spontaneous live demonstration. This highlighted the importance of extensive experience and time investment. It reminded me of a conversation with a friend about intuition.
I recalled reading a book that emphasized how intuitive judgment relies on countless practices internalized over time. However, such practice must be planned and reflective, or guided by a professional coach to identify and correct mistakes.
Below is an overview of watercolor techniques for painting grapes, along with practical suggestions. If you're interested, keep reading!
●Observing and Depicting Light and Shadow
Grapes are spherical, and observing the shifts between light and dark areas reveals the direction of the light source. The small diagram on the lower left illustrates the layers from light to dark, essential for expressing the form of the sphere. Pay attention to the junctions where shadows meet light, as these are crucial for creating depth.
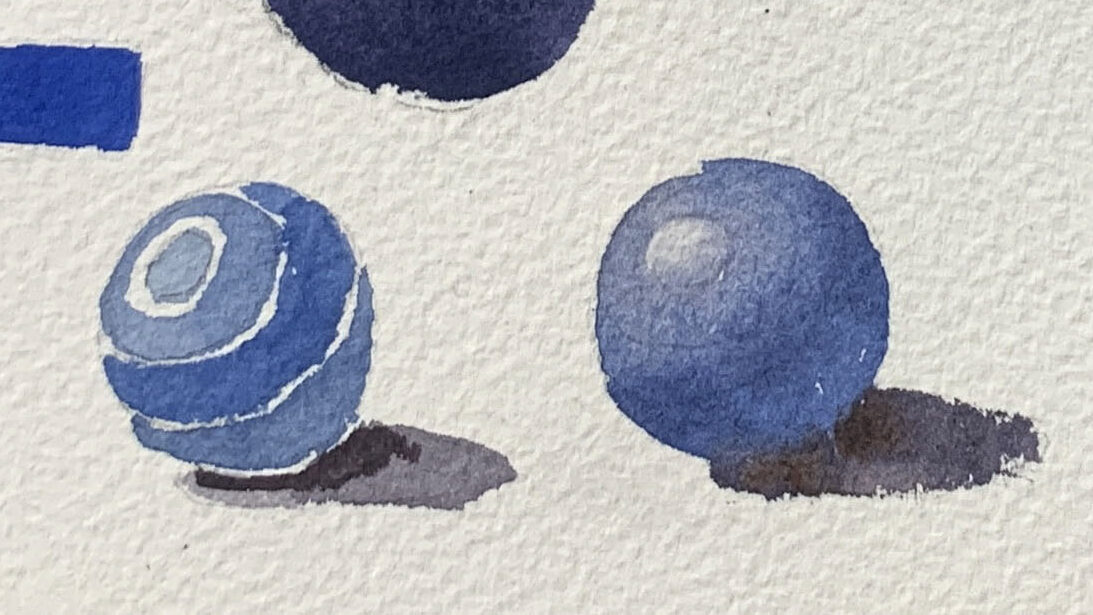

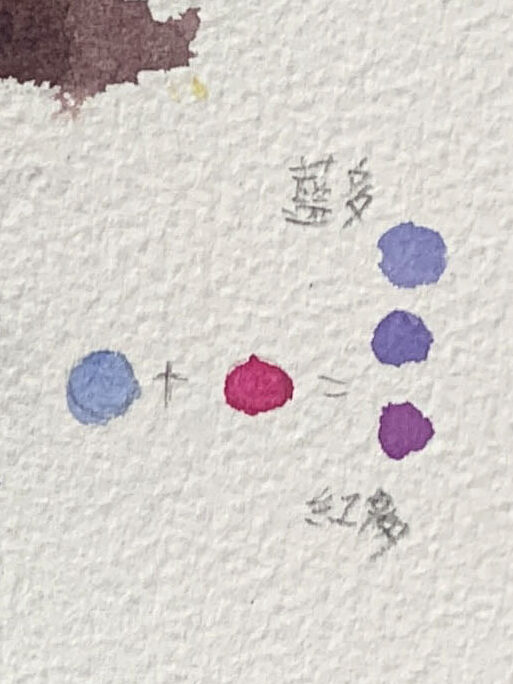
●Color Palette and Blending
The grapes are painted in cool tones (blue and purple), while another group of fruits uses warm tones (orange and red). When blending colors, maintain balance. For example, purple can lean toward either blue or red, depending on your preference.
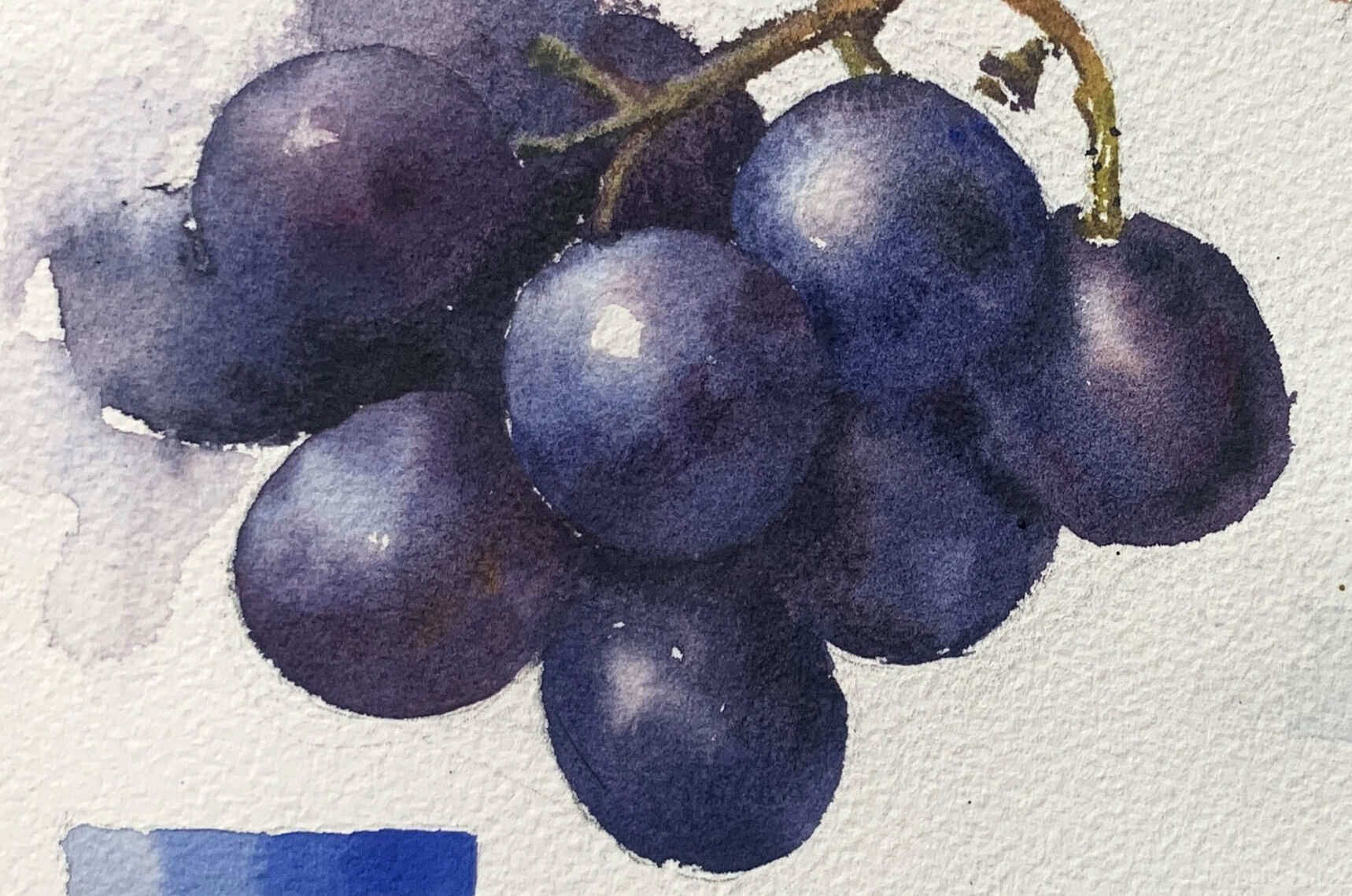
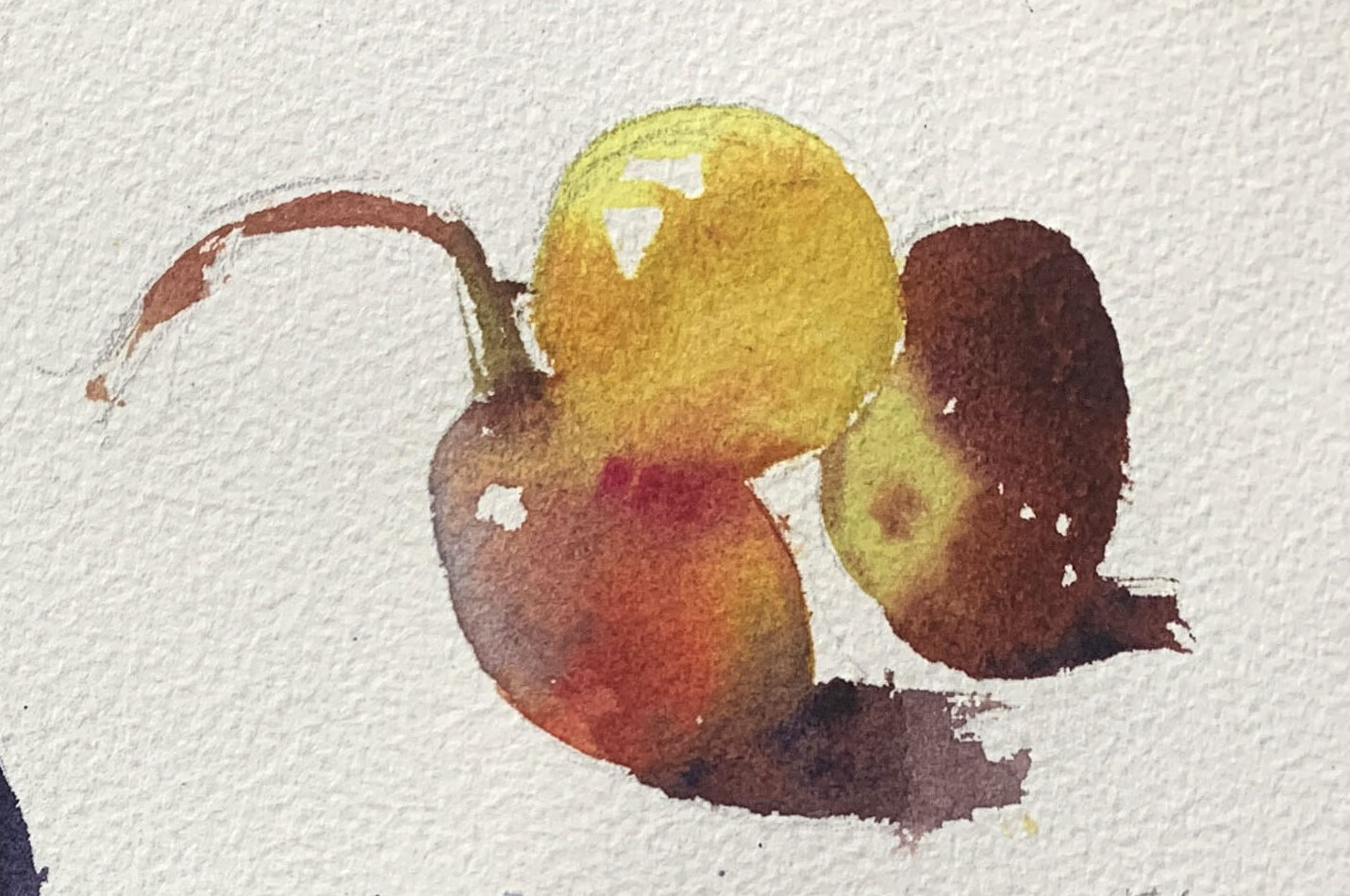


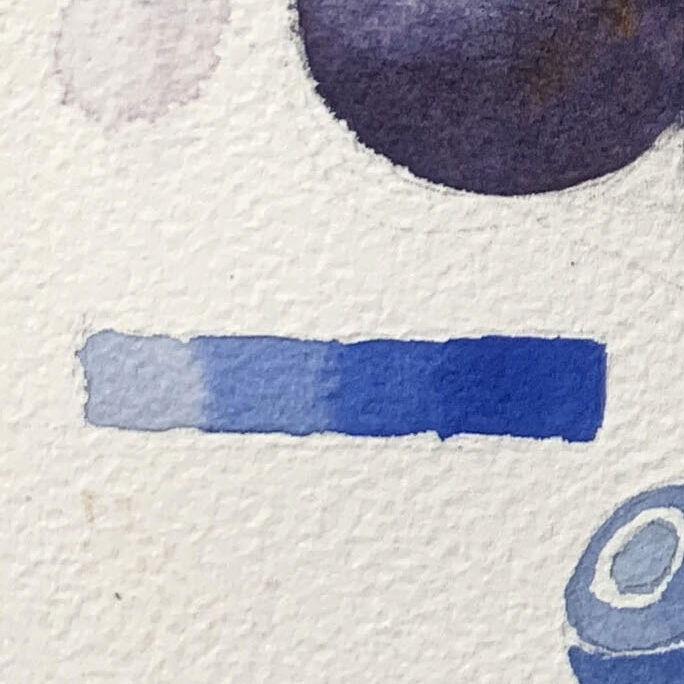
●Creating Gradients
Before starting the gradient, ensure you have enough paint prepared for the required area. Gradually build from a lighter wash with more water to a darker tone at the edges, adjusting the paint concentration on the brush as you go.

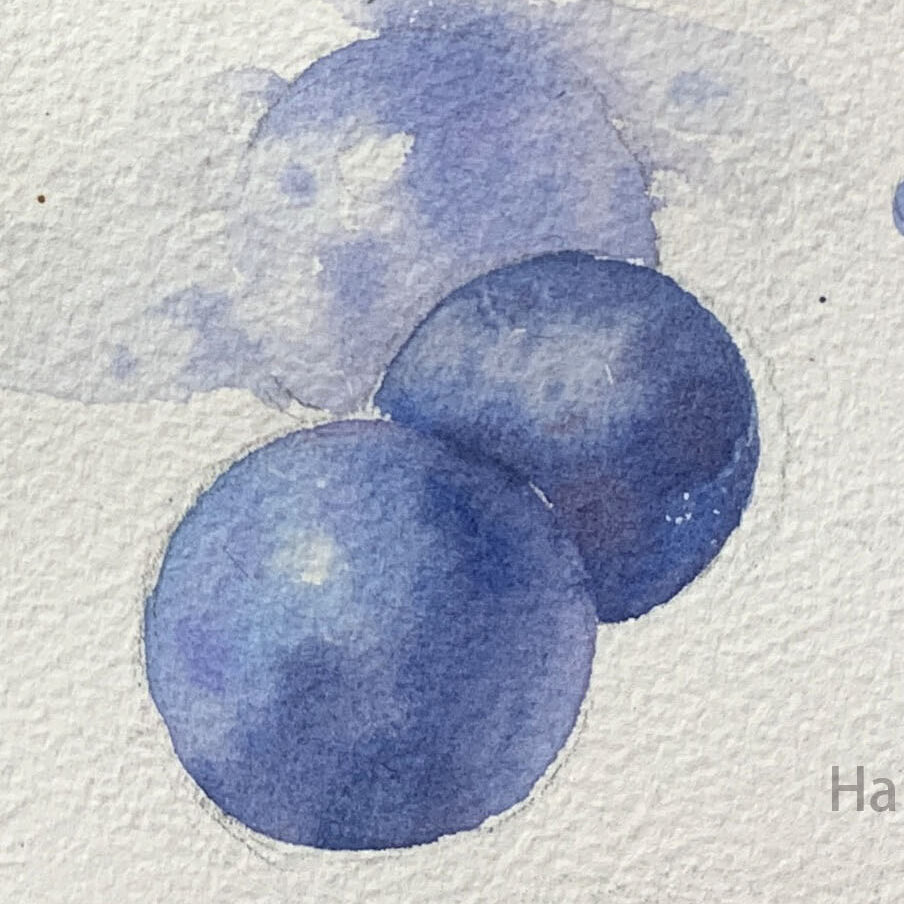
●Step-by-Step Guide
1. Sketching the Composition
Begin by lightly sketching the outlines of the grapes and other fruits with a pencil, paying close attention to their overlapping and spatial relationships.
The following painting technique introduces the method of direct color blending.
2. Painting the Highlights
Leave highlights unpainted or apply a light water wash, starting the color application around the highlight. Use more diluted paint for the lighter areas.

3. Shadows and Transitions
Observe that the color on the turning surface of the grapes is darker. Use deeper, richer blue-purple hues to emphasize the dimensionality of the sphere.
Notice the soft, blurred edge between shadows and darker areas—blend them seamlessly for smooth transitions in color.
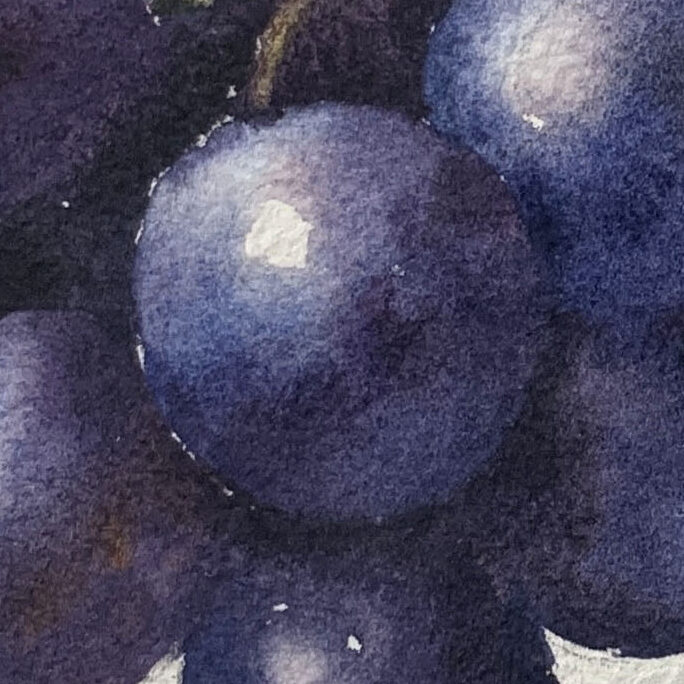

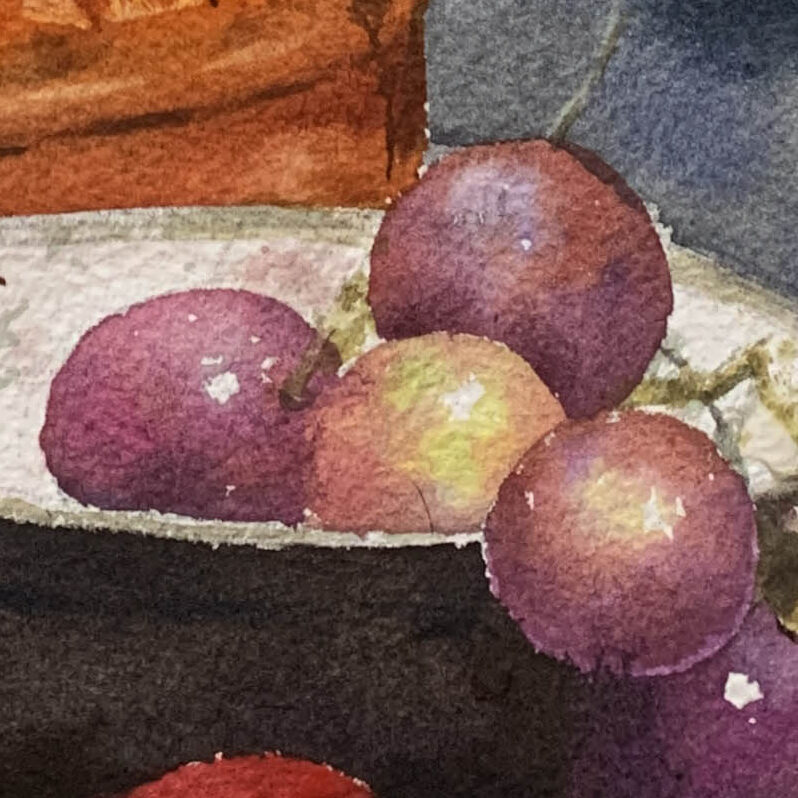
Reference for Still Life Containers: Learn Watercolor by Watching Demonstrations
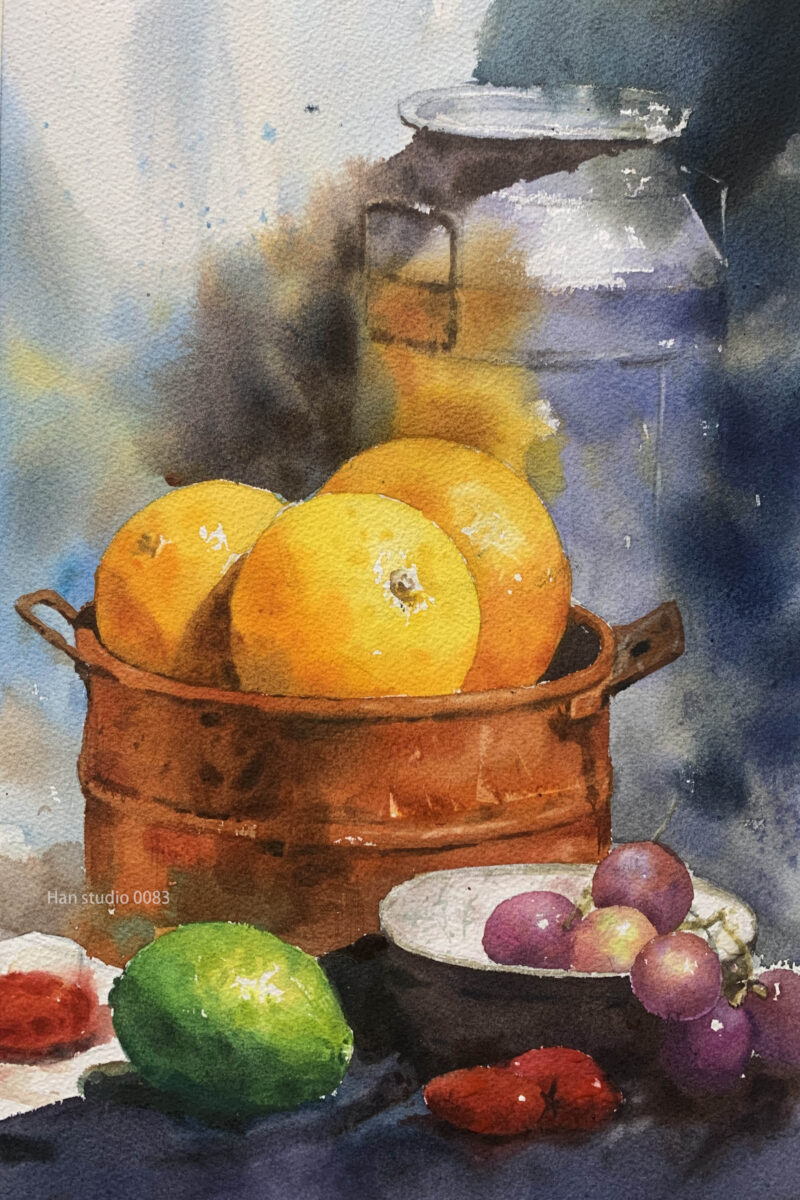
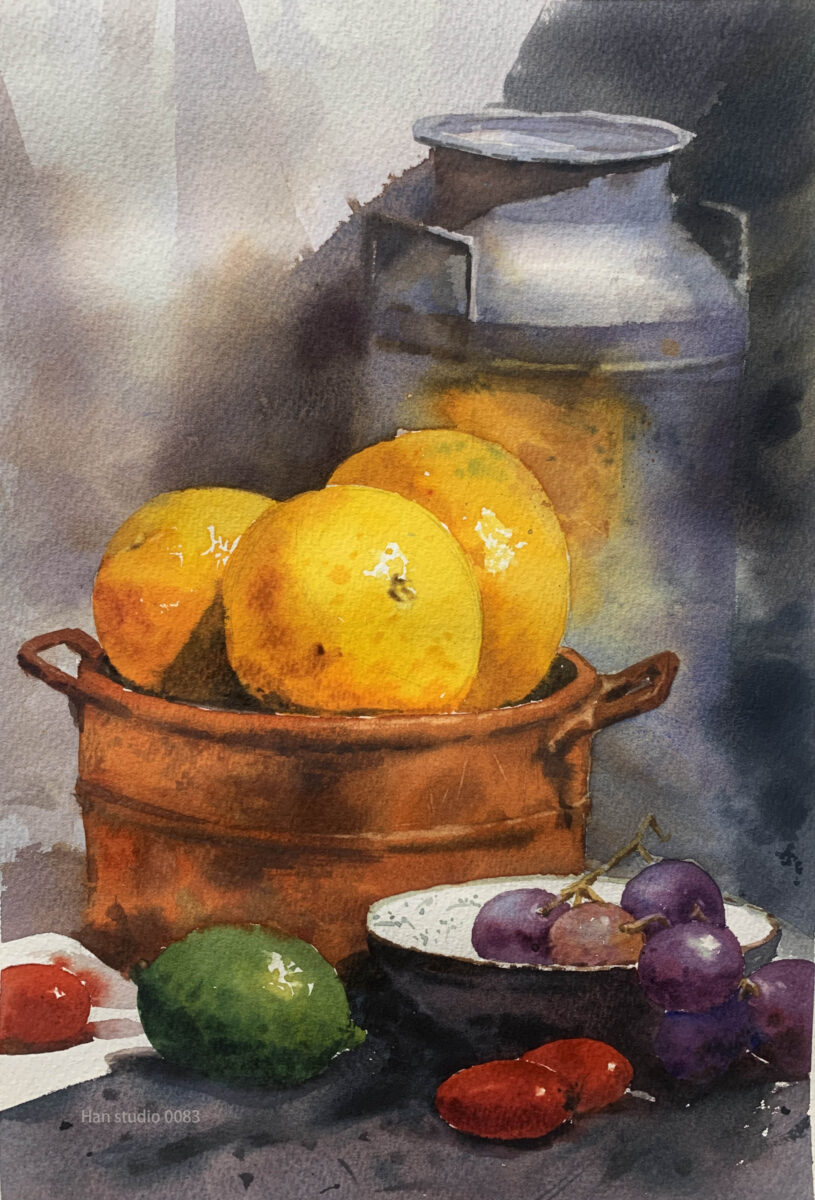
We hope this watercolor guide helps you understand the nuances of painting grapes. If you have specific topics you'd like us to cover or other painting techniques you wish to explore, feel free to leave a comment or message us. Happy painting!
If you're interested in learning to draw but don't know where to start, or if you'd like to understand the knowledge behind drawing,
feel free to join my LINE and contact me. In my classes, I organize drawing methods in a clear and structured way.
Click here to learn more about my drawing courses!
Other Related Watercolor Articles:
Watercolor Mixing Tips: Achieve Natural Transitions Easily
How to Paint the Light and Dark Layers of a Monstera Leaf