In the process of learning portrait drawing, the ear is often a part that gets ignored — or even skipped altogether.
Although the structure of the ear doesn’t carry expressions like other facial features, its three-dimensional form is clear.
Learning to observe and break down the ear not only makes your portrait drawing more complete but also helps you accurately grasp the tilt and rotation of the head.
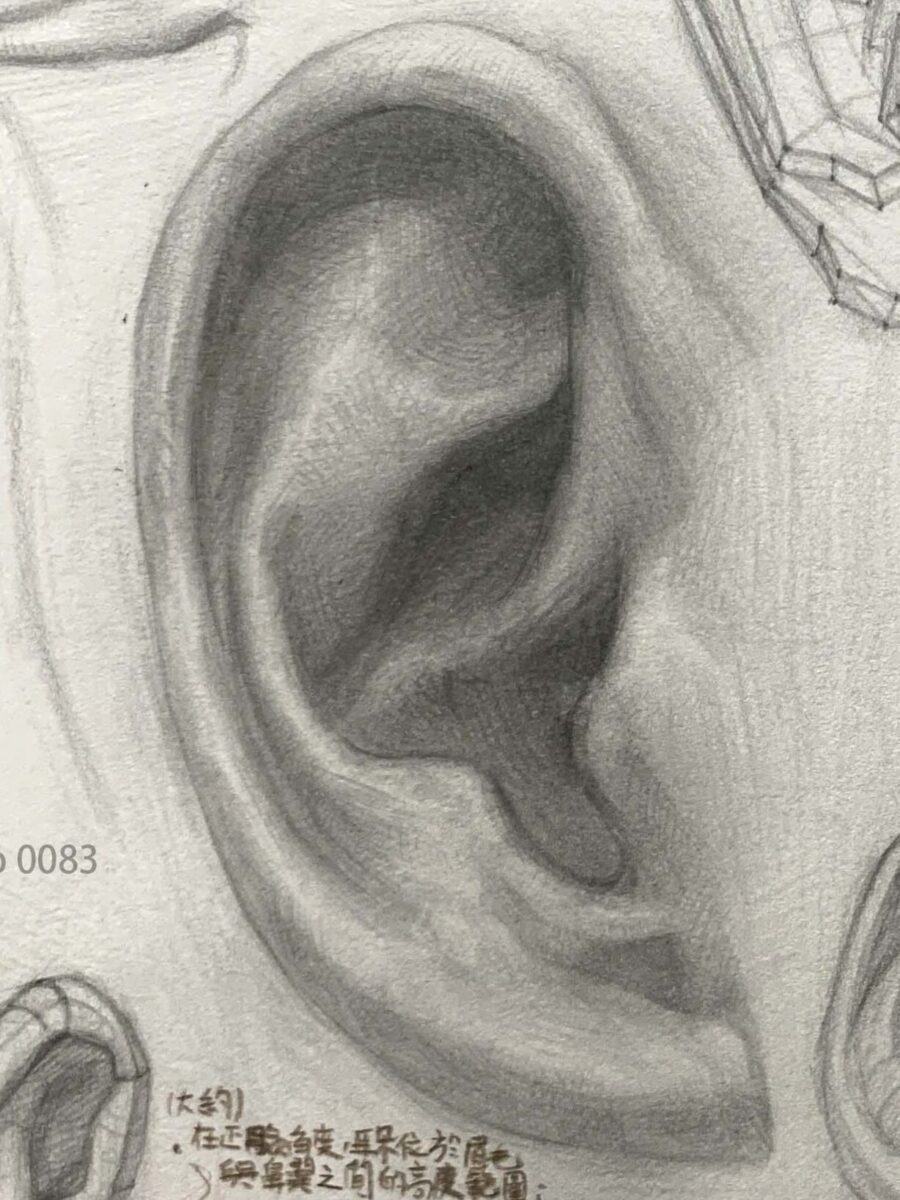
Basic position and proportion of the ear
The ear isn’t just randomly attached to the side of the head — it has general reference points (though the exact position varies from person to person):
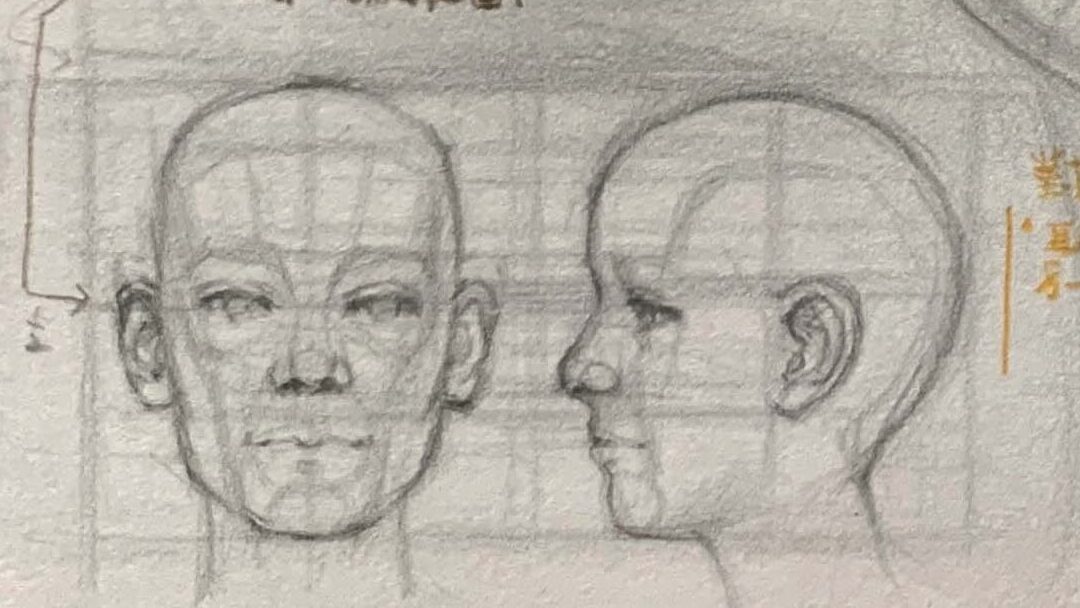
- The top of the ear aligns roughly with the eyebrows, and the bottom aligns with the base of the nose — a common reference when viewed from the front.
- From a side or upward angle, the ear shifts slightly backward, positioned between the midline of the head and the back of the skull.
| Reference Points | DescriptionDescription |
|---|---|
| Upper boundary | roughly aligns with the eyebrows or the upper corner of the eyes. |
| Lower boundary | roughly aligns with the base or the wings of the nose. |
| Front–back position | the ear is not flatly attached to the face but embedded in the concave surface of the temporal bone, tilting backward about 15°–20°. |
📍 Key observation
In the front–side structural view, the ear’s front–back position corresponds exactly to the “rear turning point of the mandible,” which is an important clue for understanding the spatial turn of the head.
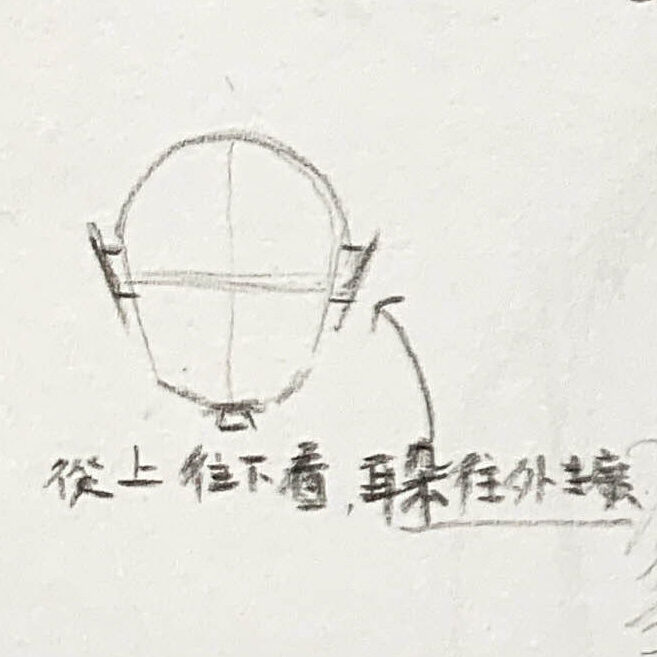
- Practical tip: When sketching the draft lines, first mark the general contour and tilt direction of the ear. This helps you position the facial features and overall head structure more accurately.
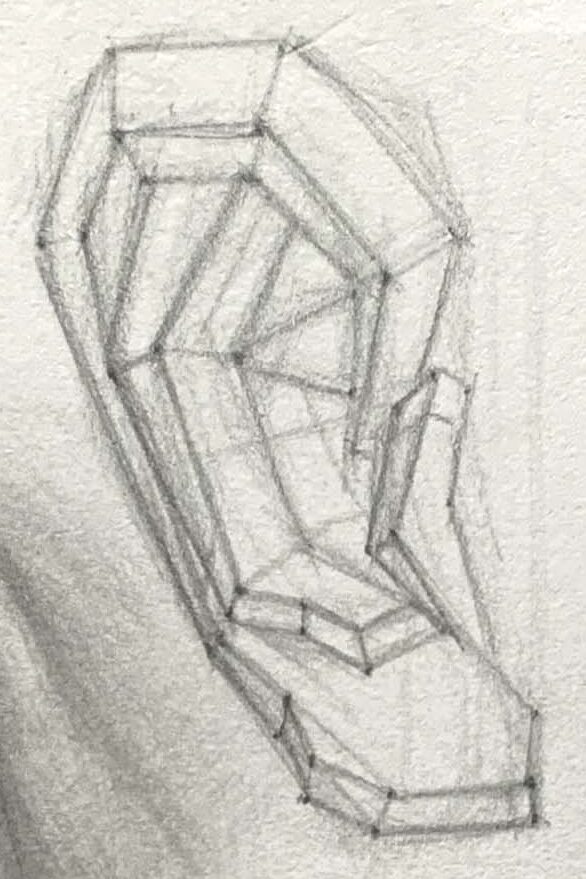
Below, I’ve broken the ear down into three main parts to help us understand its shape characteristics.
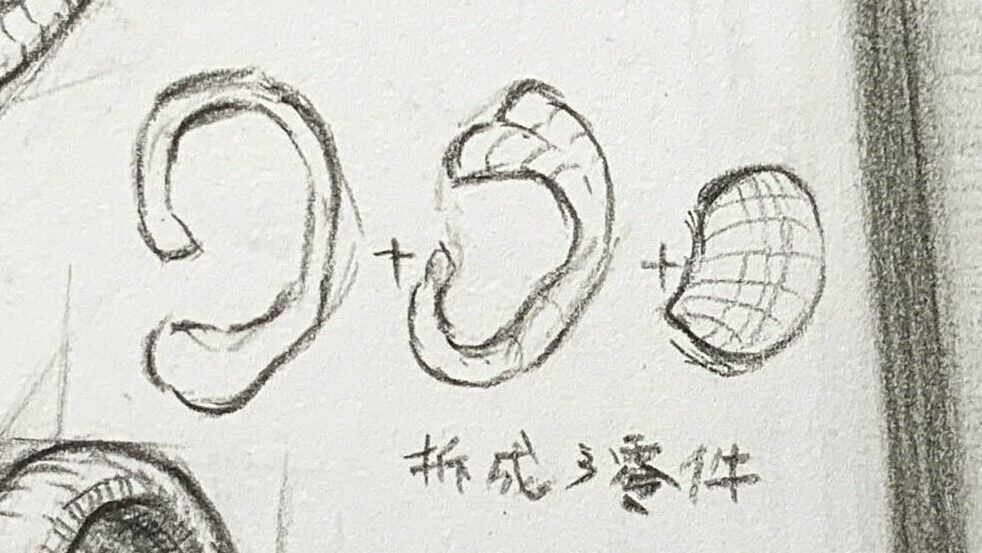
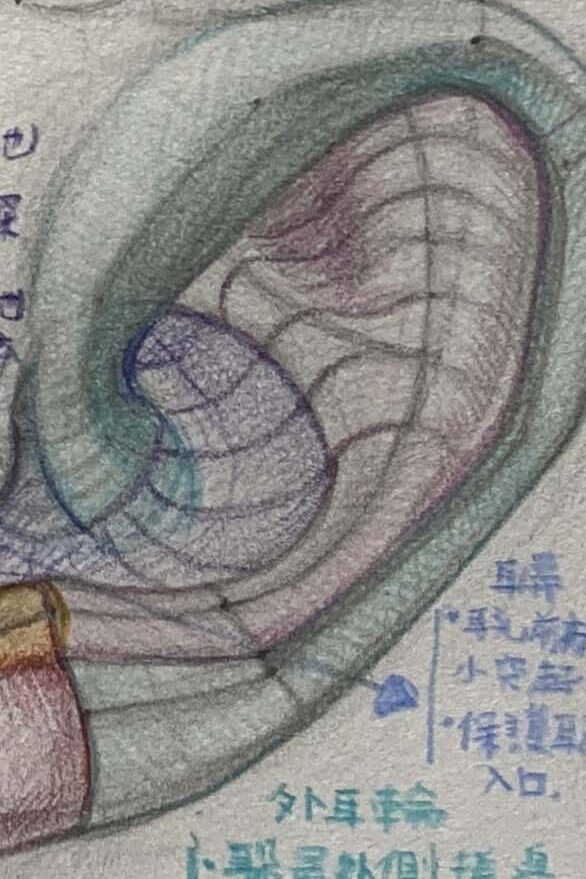
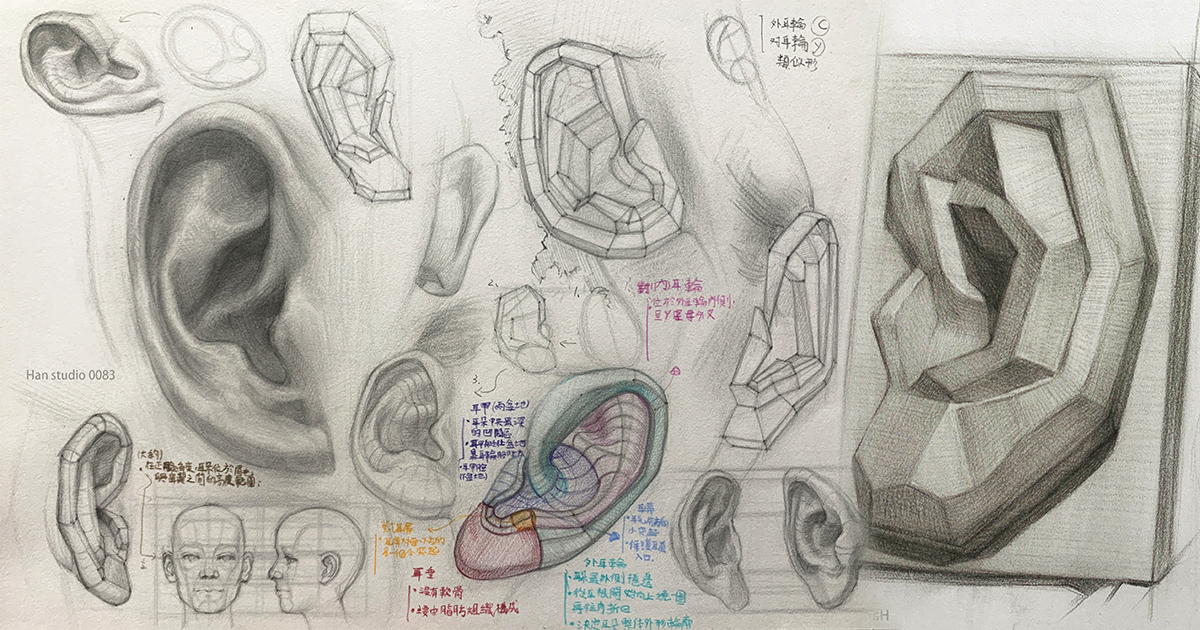
Our ears, also called the auricle, are composed of the following parts:
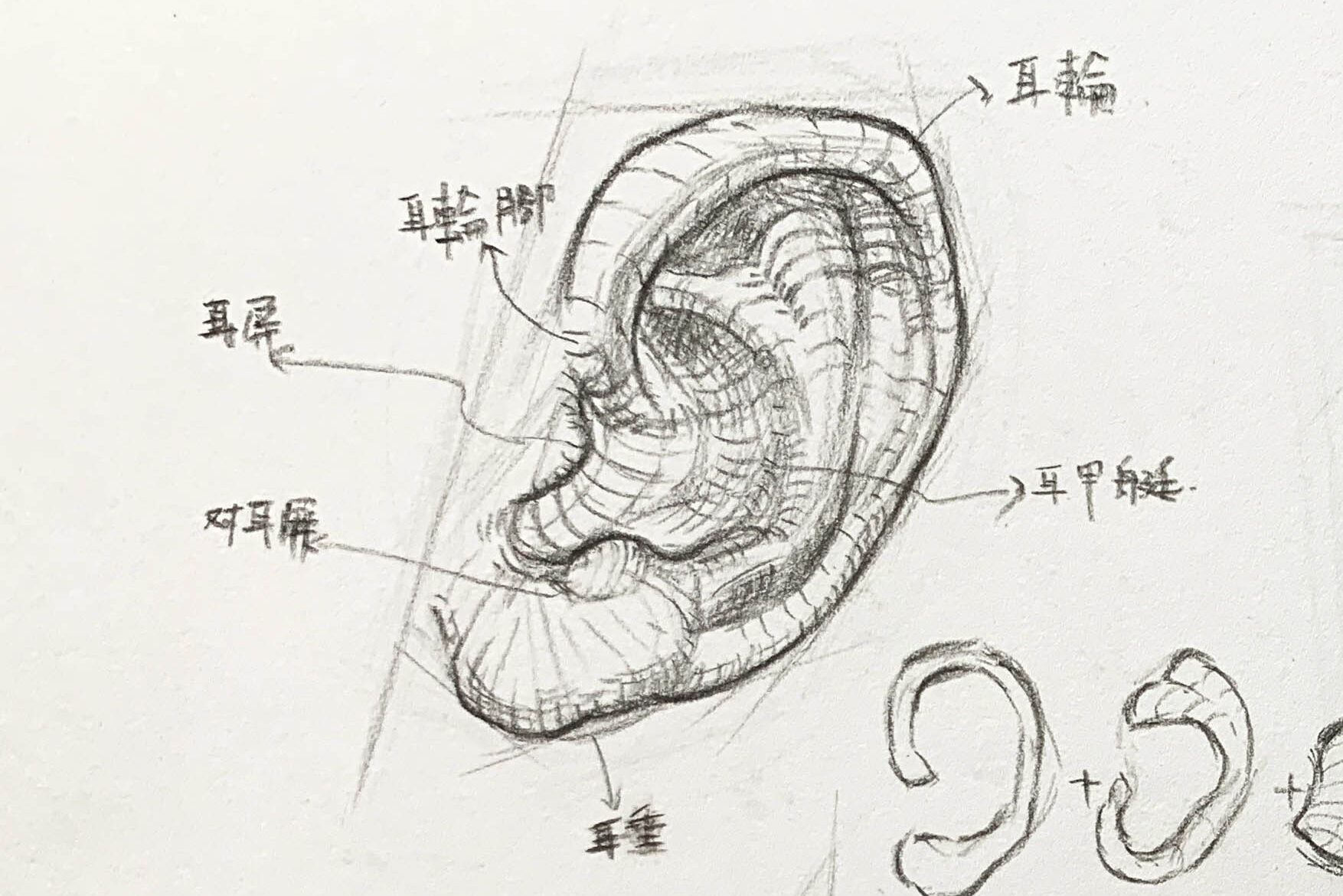
Observation method for the five major structural areas of the ear
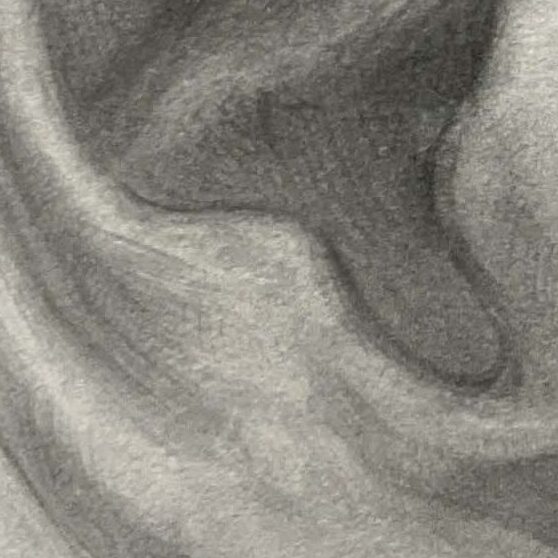
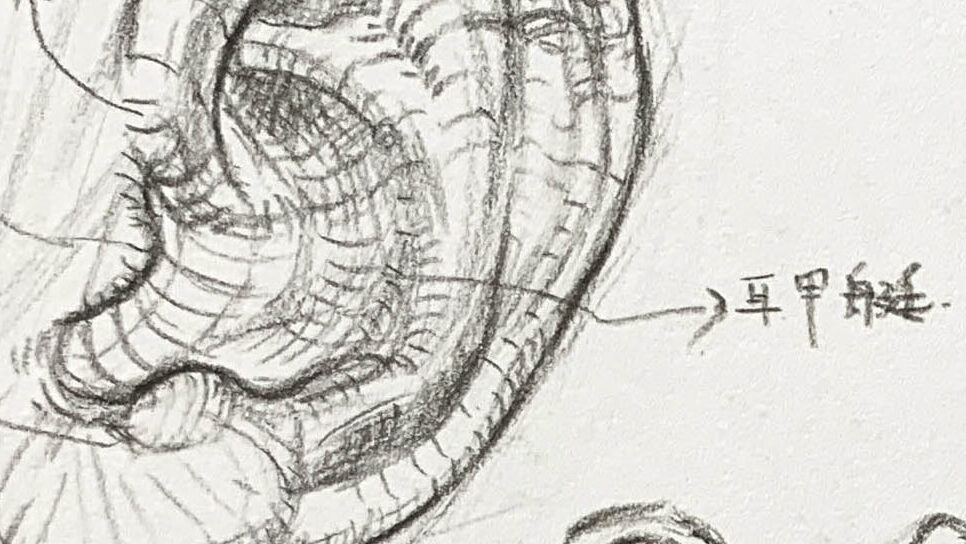
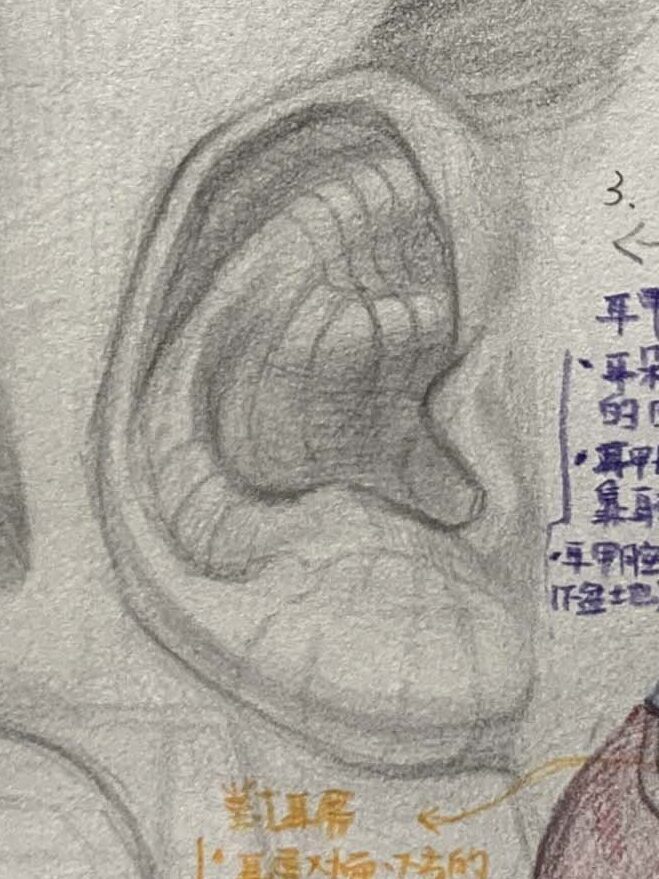
● Helix:
The most prominent outer curve of the ear, forming an arc around the ear. The helix outlines the ear, and it’s important to pay attention to its curvature and the shadows formed by its folds.
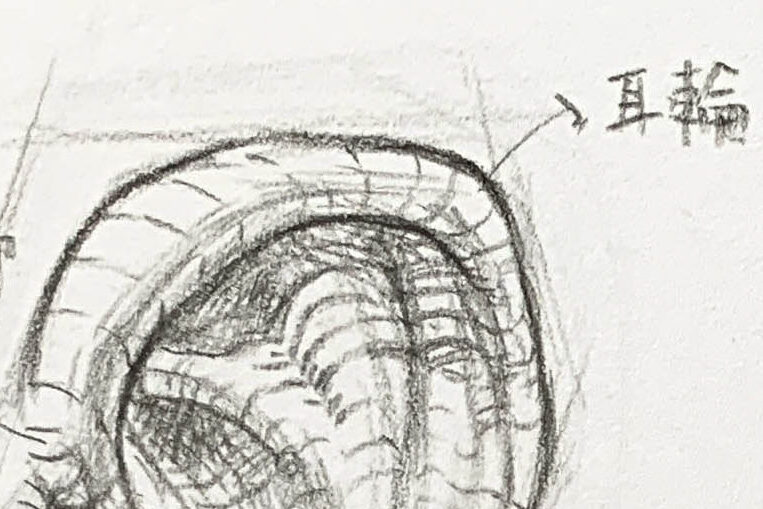
Antihelix:
The raised structure on the inner side of the helix has a Y-like shape, usually divided into upper and lower branches, supporting the ear’s overall form.

- The inner second ridge, shaped like rolling hills, divides into two branches: the superior and inferior crus.
- It is the key to the ear’s sense of depth; its curvature is visible from both front and side views.
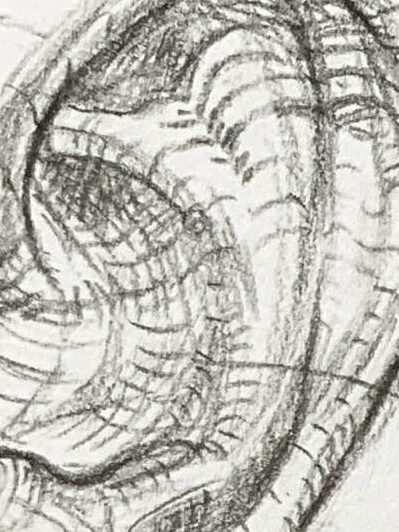
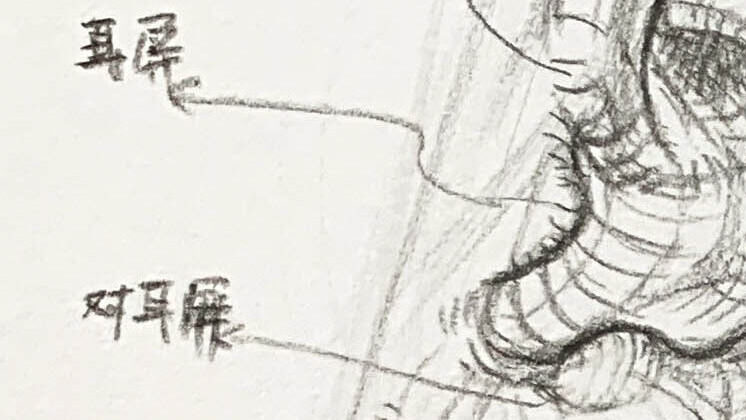
Tragus – position and shape
From the side view, it partially covers the entrance of the ear canal.
Shape: A small triangular or crescent-shaped cartilage projection, with a slightly thicker front edge, a smooth outer side, and an upper edge that forms a small curved notch with the antitragus. This notch is called the intertragic notch.
- Function:
- Protective function — blocks some noise and dust, protecting the ear canal entrance.
- Sound guidance — reflects sound waves, helping distinguish front and back sound directions.
- In 3D modeling or portrait drawing, the tragus roughly indicates the “center of the ear canal.”
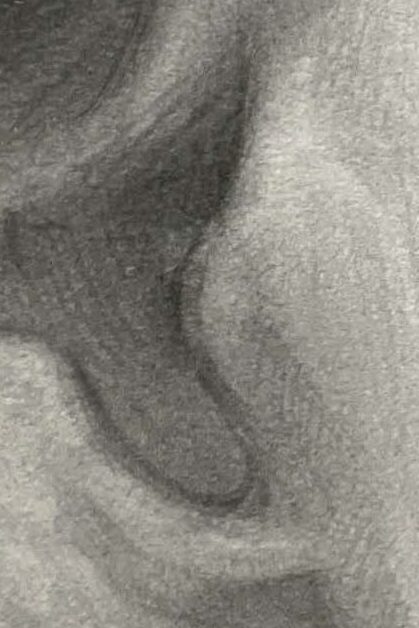
Tragus – form and volume structure
Antitragus
位置:
在 耳屏 的 對面、稍下方,
位於耳垂上方、耳甲腔的外側邊緣。
Shape:
一個A small oval or triangular cartilage projection,,
Slightly tilted forward and upward, forming a “V-shaped notch” with the tragus.

Function:
- Protects the ear canal — together with the tragus, forms an outer guard around the canal.
- Reflects sound — helps in identifying sound direction, especially from behind.

Antitragus – form and volume structure
Cymba conchae:
The hollow area inside the ear, situated between the helix and antihelix, which helps funnel sound into the ear canal. It resembles a satellite dish or bowl.

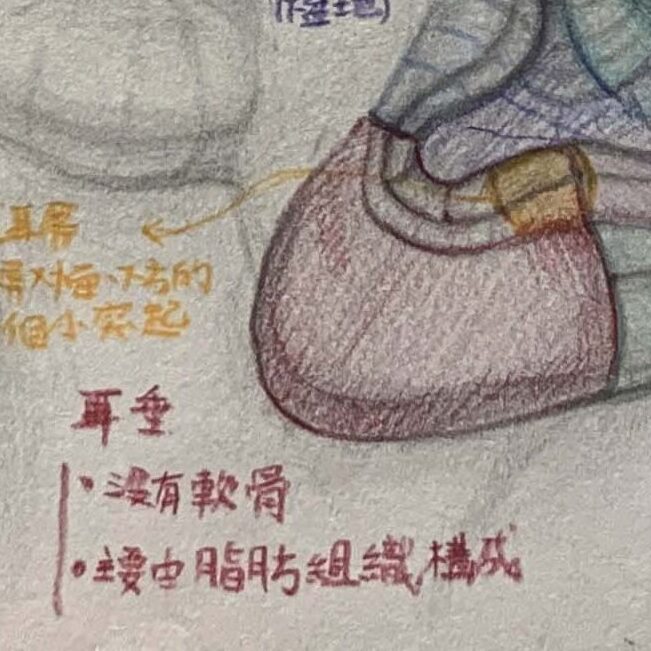
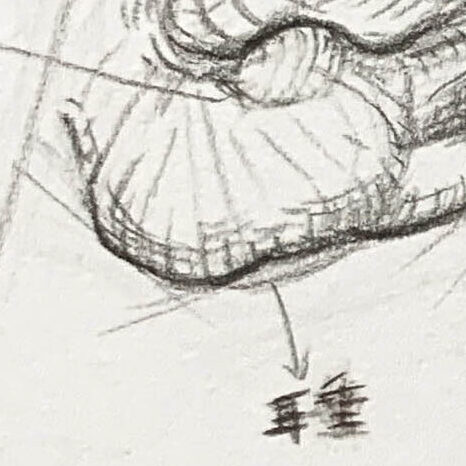
Earlobe:
Dorsal Fin (Top Fin):The lowest part of the ear, connected beneath the antitragus.
Structure::
- The only part of the ear without cartilage;
- Composed of skin, fat, and a small amount of connective tissue;
- Rich in blood vessels, soft to the touch, and highly flexible.
Attachment point — connects to the head in front of the jaw angle, marking the boundary between the helix and the side neck skin.
Drawing and observation key points
| Viewpoint | Features and depiction |
|---|---|
| Front view | the earlobe almost touches the side of the lower face; highlights appear soft. |
| Side view | hangs in a semi-oval shape with smooth edges, forming a gentle curve with the jawline. |
| Three-quarter view | the earlobe appears as a light oval, serving as the natural ending of the helix. |
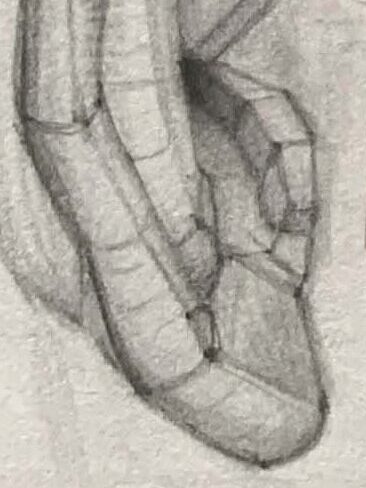
The soft, rounded lower part of the ear, lacking cartilage. The thickness and shape of the earlobe vary among individuals.
●How to Draw Ears:
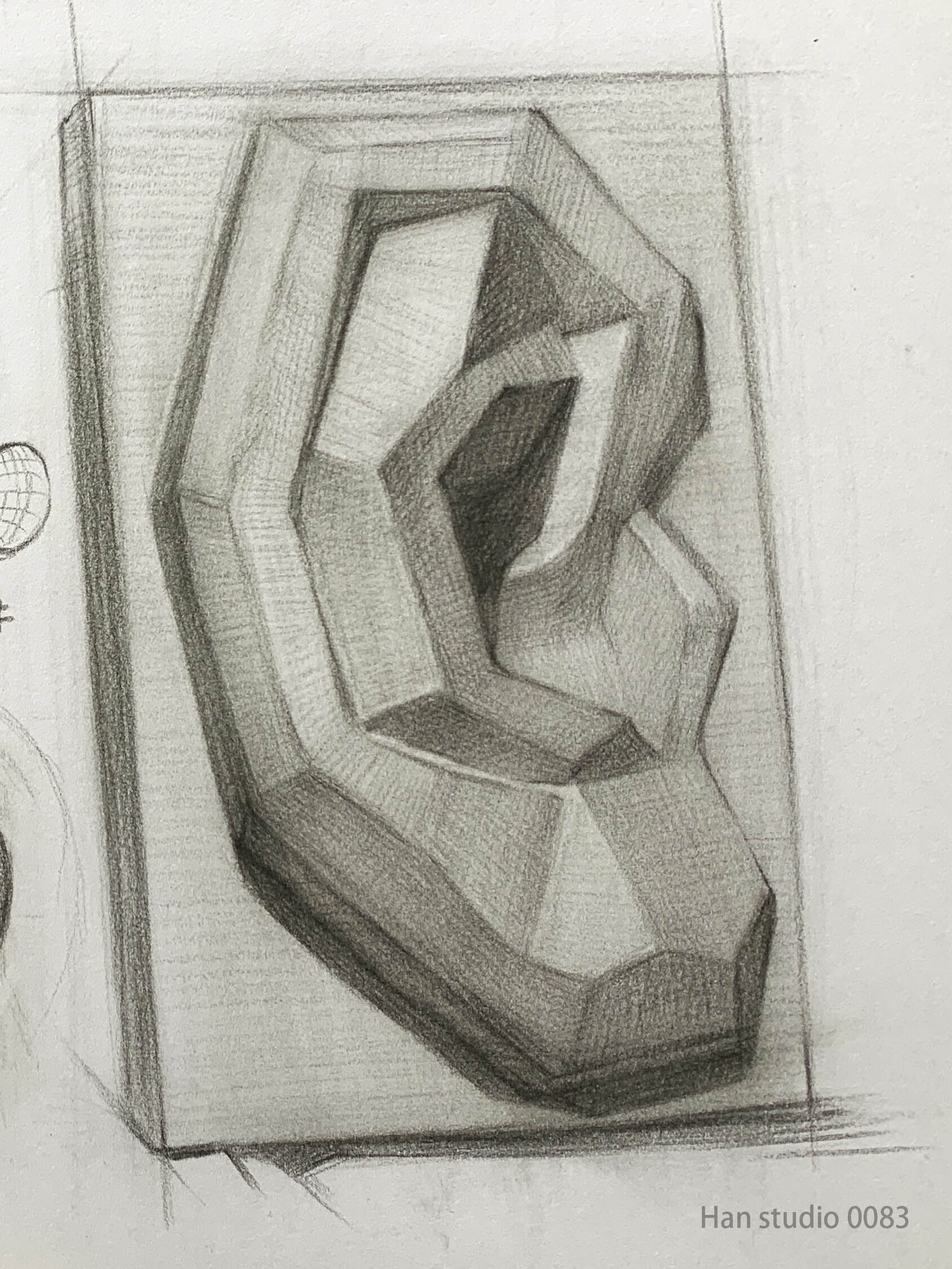
The plaster model of an ear on the far right simplifies the curves into planes, which can help us understand the areas' transitions.
It’s recommended to study a plaster ear model before drawing real ears to get a sense of the basic shapes.
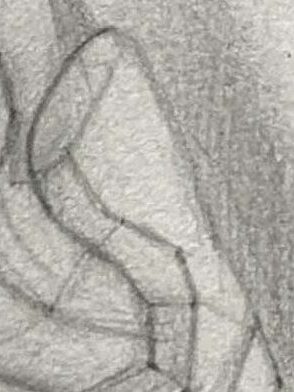
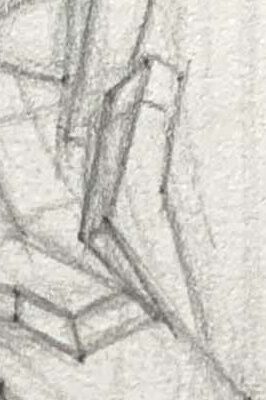
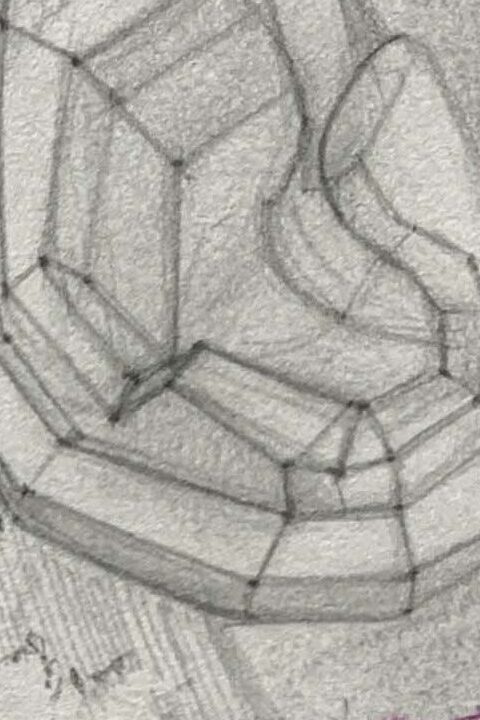
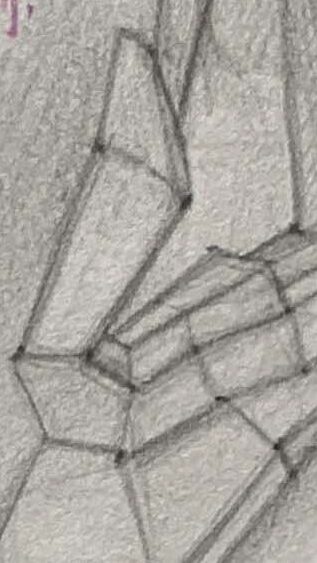
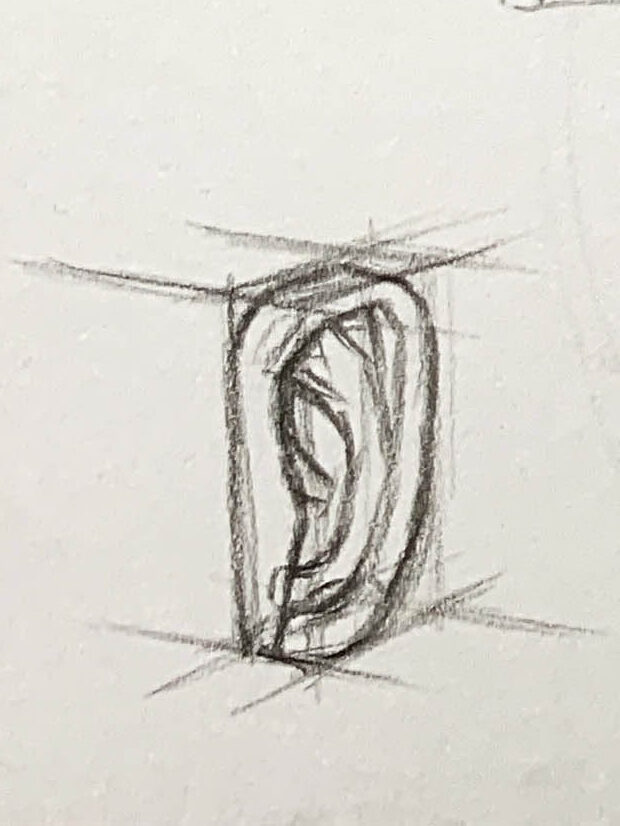
1.Simplify the Outline:
Start with simple geometric shapes (like circles and ovals) to sketch the general shape of the ear, marking the positions and characteristics of the helix, antihelix, tragus, and earlobe.
You can also use rectangles to assist in drawing ears from different angles, helping you understand the ear's geometric forms.
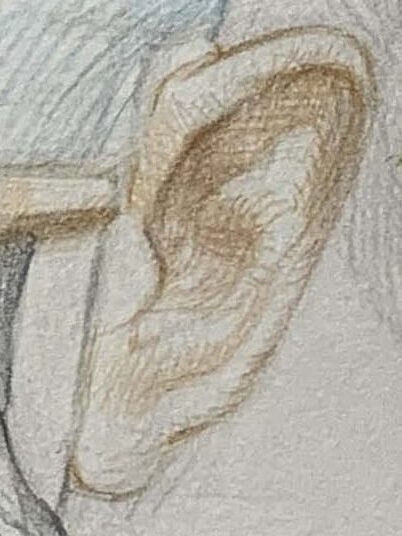
2.Refine the Structure:
Once the outline is complete, add structure lines to capture the rises and falls between the helix and antihelix.
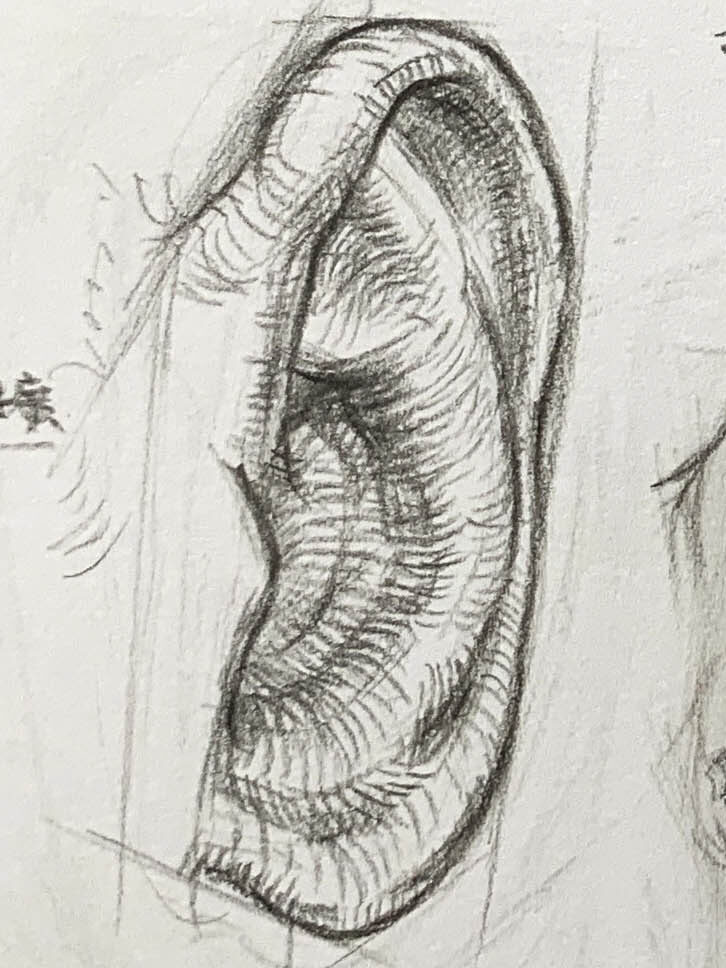
3.Enhance the 3D Effect:
Use shading to emphasize the ear’s contours, focusing on the intersections of the helix, antihelix, and tragus. Observe how even small shadowed areas can create depth.
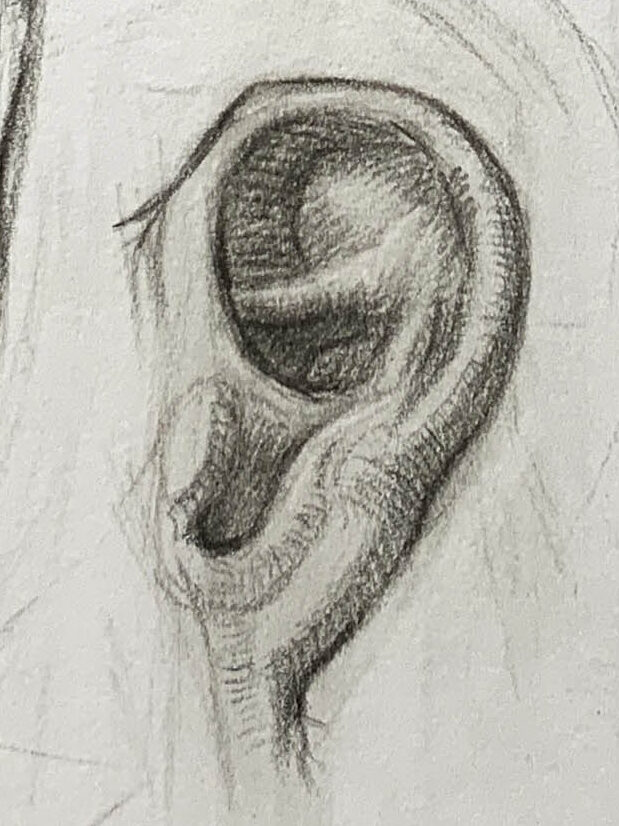

Shape changes of the ear from different angles
Front view: only a small portion of the ear is visible, and the helix becomes the most prominent contour line.
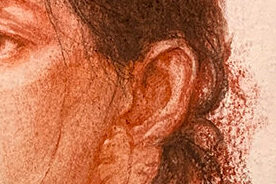
Side view: the entire ear is visible — this is the best angle for studying its structure.
Three-quarter view (45°): the ear appears slightly compressed, but the directions of the helix and earlobe remain identifiable.
Upward and downward angles: The ear shifts noticeably up or down depending on the tilt of the head; observing the crossing directions of the helix and antihelix is the key to judging the angle.
I hope this guide helps you understand ear structure and drawing techniques. If there are any topics you’d like to see or specific drawing methods you'd like to learn, feel free to leave a comment or message me. Happy drawing!
If you're interested in learning to draw but don't know where to start, or if you'd like to understand the knowledge behind drawing,
feel free to join my LINE and contact me. In my classes, I organize drawing methods in a clear and structured way.
Click here to learn more about my drawing courses!
Want to explore more articles on extended drawing techniques?
How to Draw Arms: Learn Arm Movements and Bone Proportions
How to Use Two-Tone Shading: Simple Shadow Techniques
How to Sketch Facial Muscles: Capture Realism and Expression
How to Draw Masks: Use Perspective and Shadows
How to Accurately Master Hand Proportions and Joint Structure
Building Up from Simple Contours to Detailed Eye Portraits
Capturing Realism in Lip Drawing: Key Structures and Shading
Understanding the Three Key Elements of Head Structure
Mastering the basic proportions and structure of portrait drawing

Leave a Reply