During the process of painting flowers, I encountered questions about how to depict petal folds and how to coordinate the colors of flowers with the background. Here, I share my thoughts on painting flowers, using lilies as an example.
Understanding the Basic Structure of Lilies Before Painting Petals:
Characteristics of Lilies:
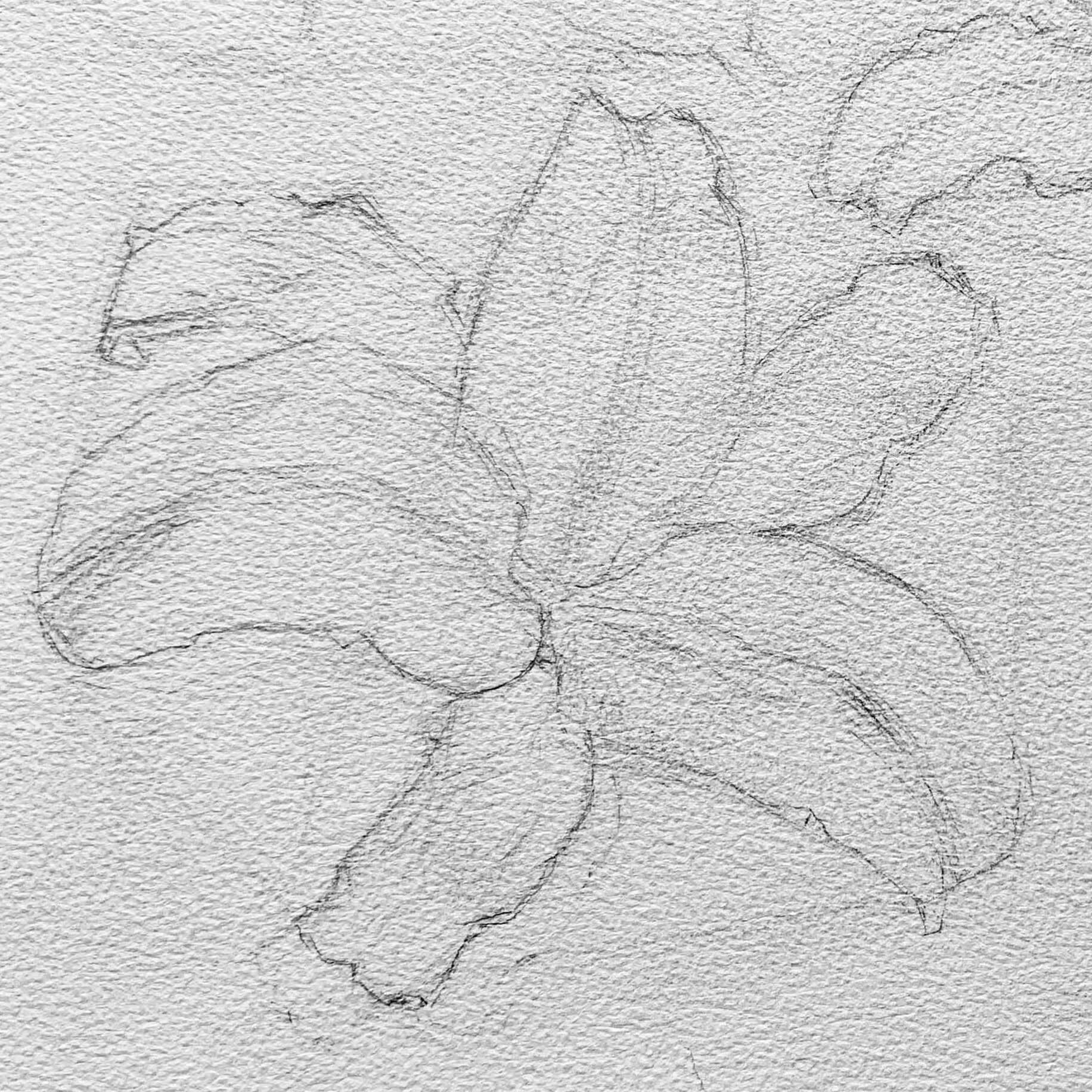
Lilies typically have six petals arranged in a structure similar to two inverted triangles, with the following features:
- The petals are long and slightly curved, with the tips curling inward or outward.
- The stamens protrude, usually consisting of six filaments with dark-colored pollen at the tips.
- The center of the petals has variations in color, sometimes including textures, gradients, or speckles.
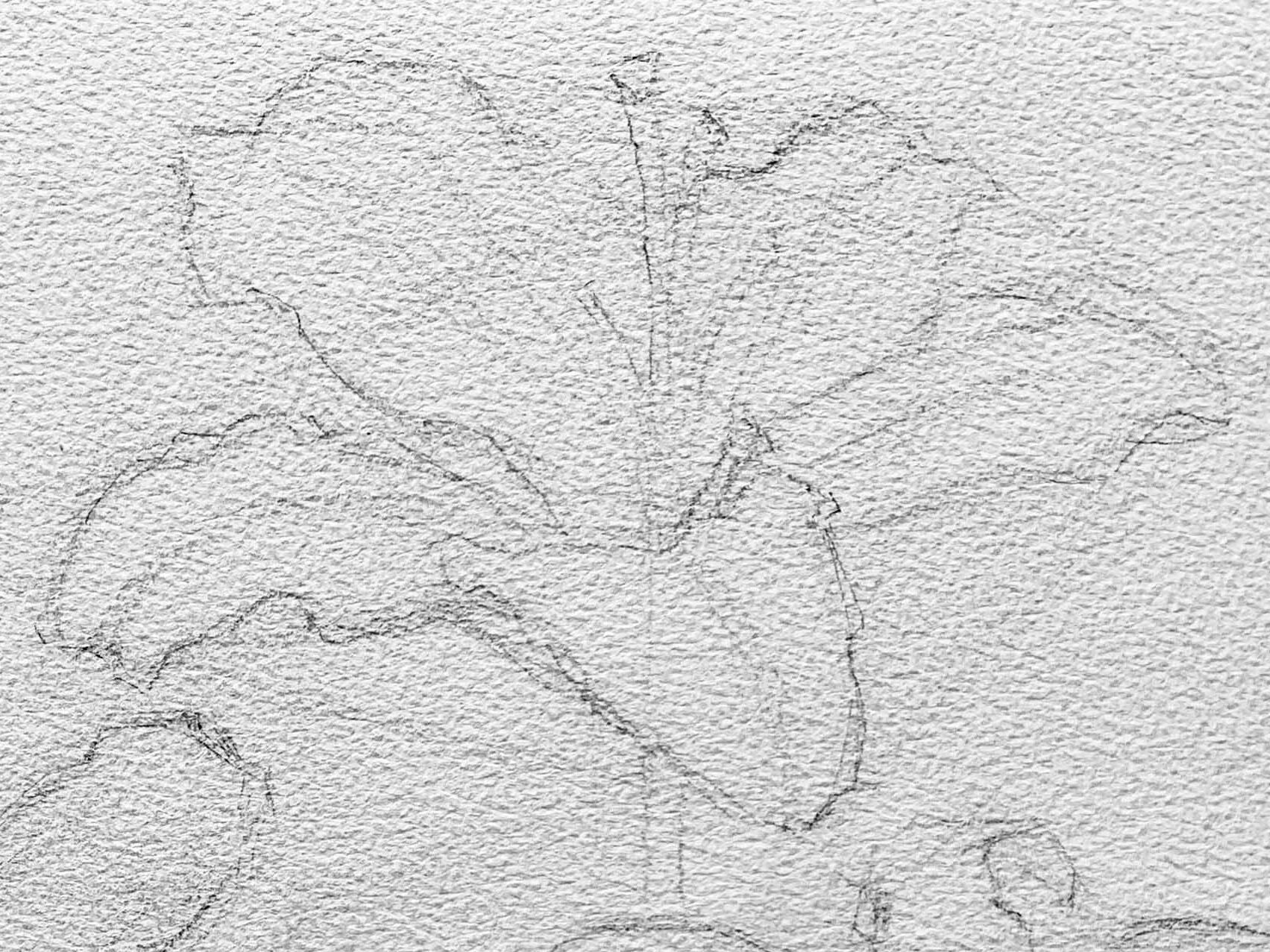
Sketching the Initial Outline
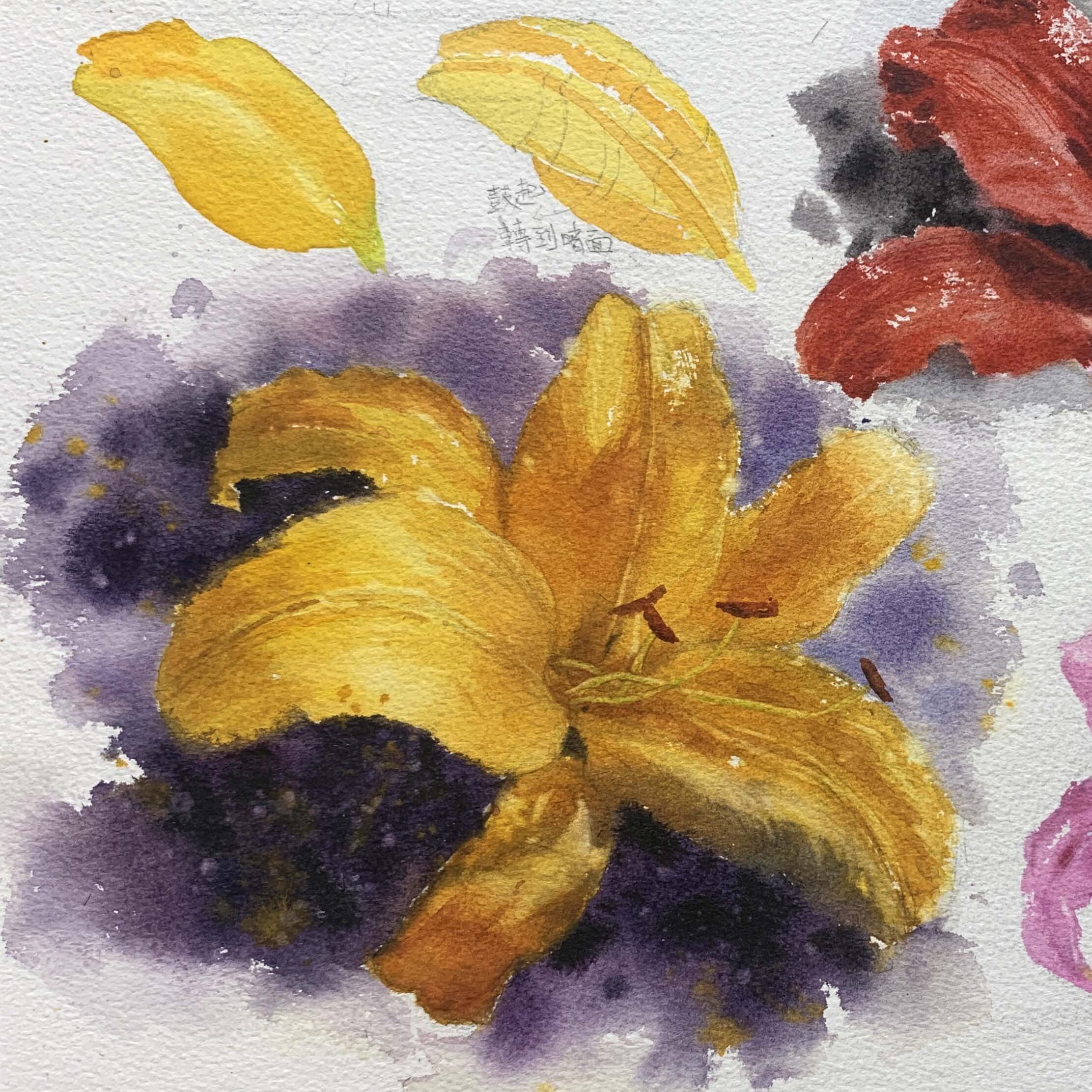
Before painting a lily, simplify its overall shape. As shown in the example image, you can start with a hexagonal shape to determine the angles between the petals, using straight lines to mark the inclinations.

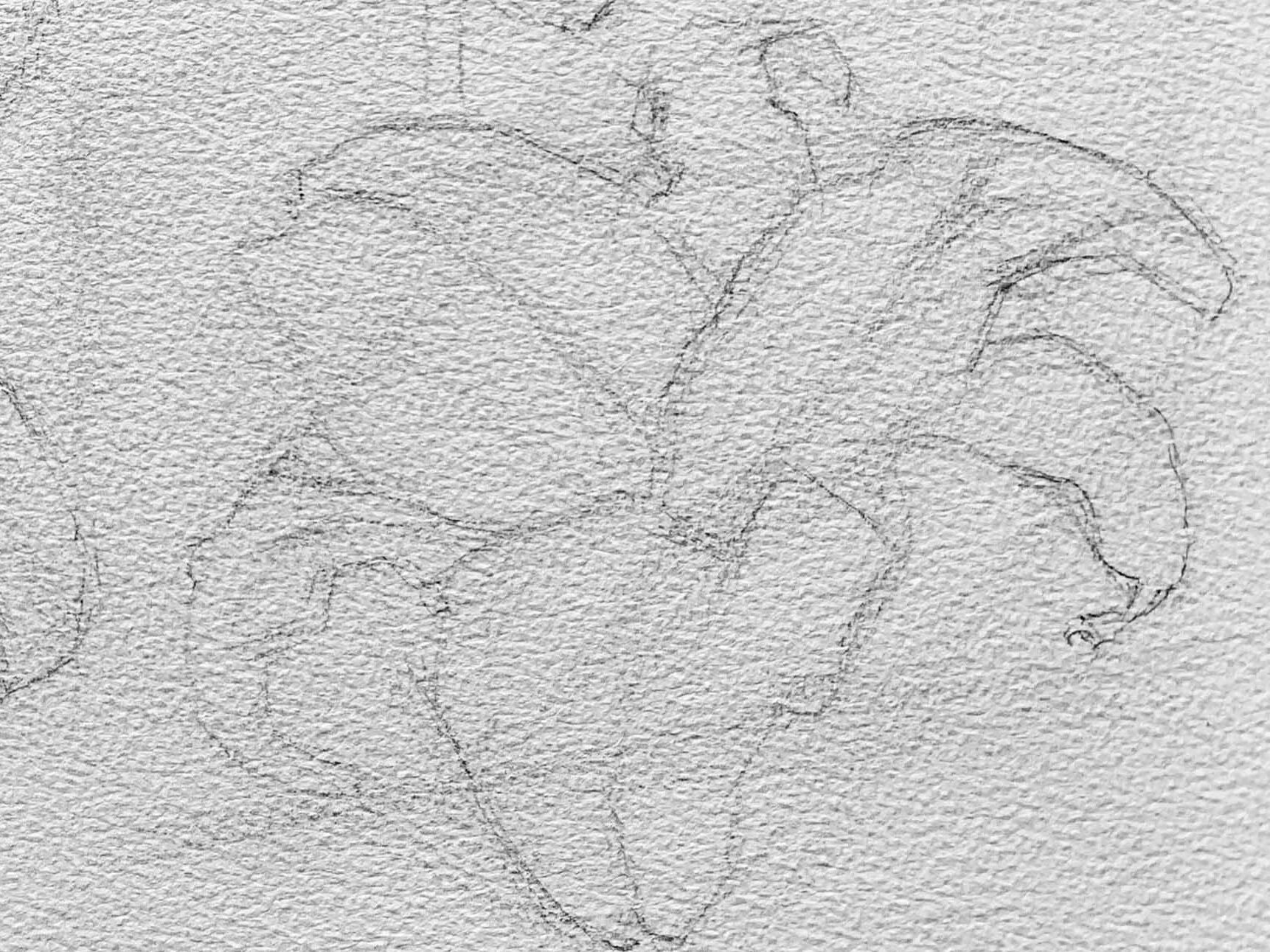

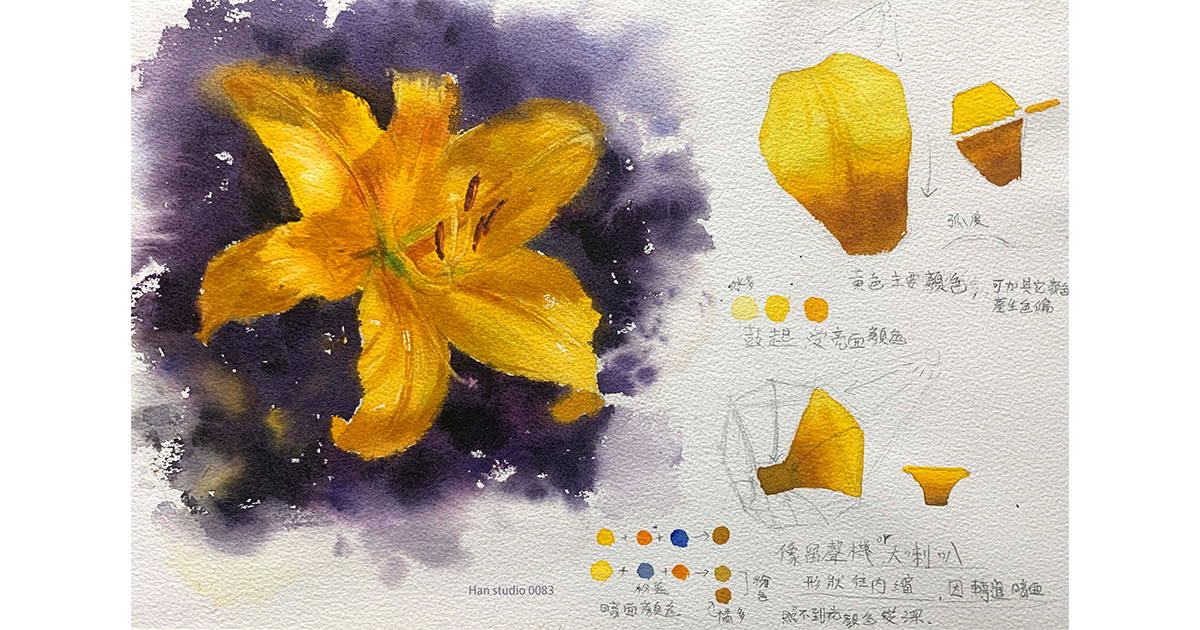
How to Use Colors to Depict Petals
Taking the example from the demonstration image: The overall shape of a lily resembles a gramophone or a trumpet. Due to the inward contraction at the base of the flower, the color of the petal interior is usually darker.
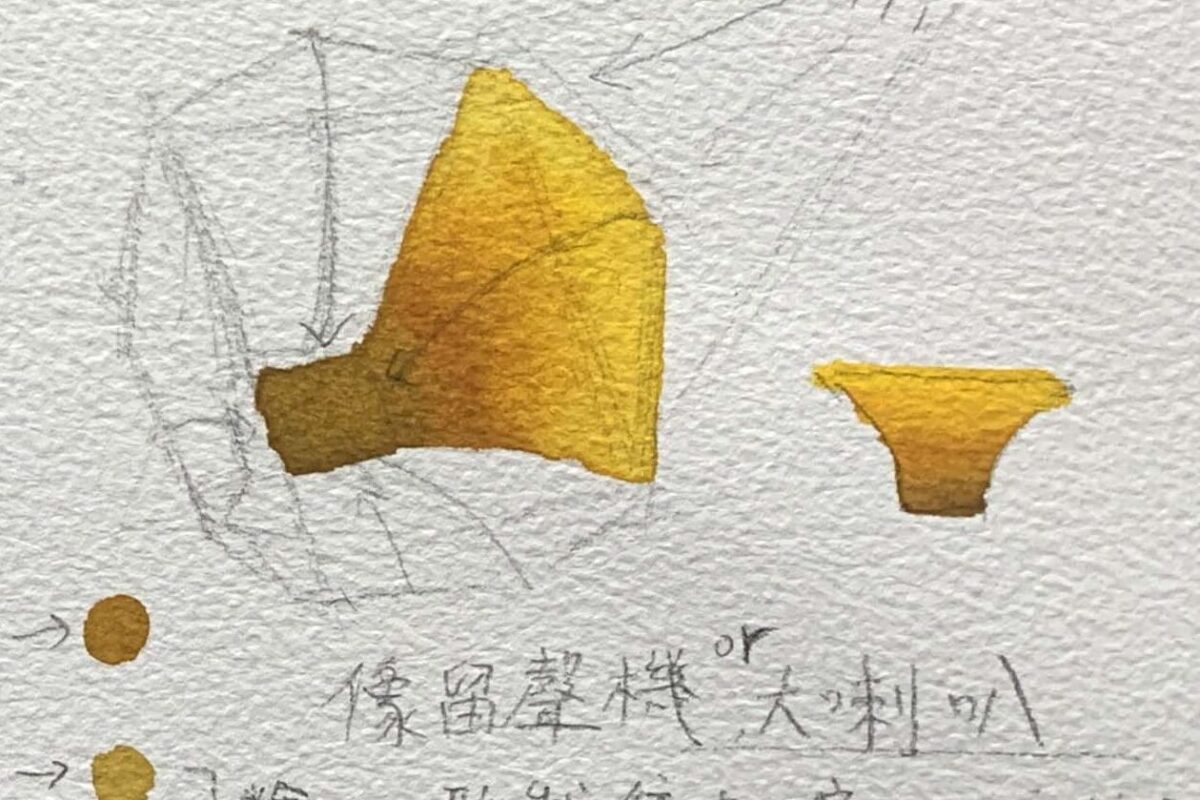
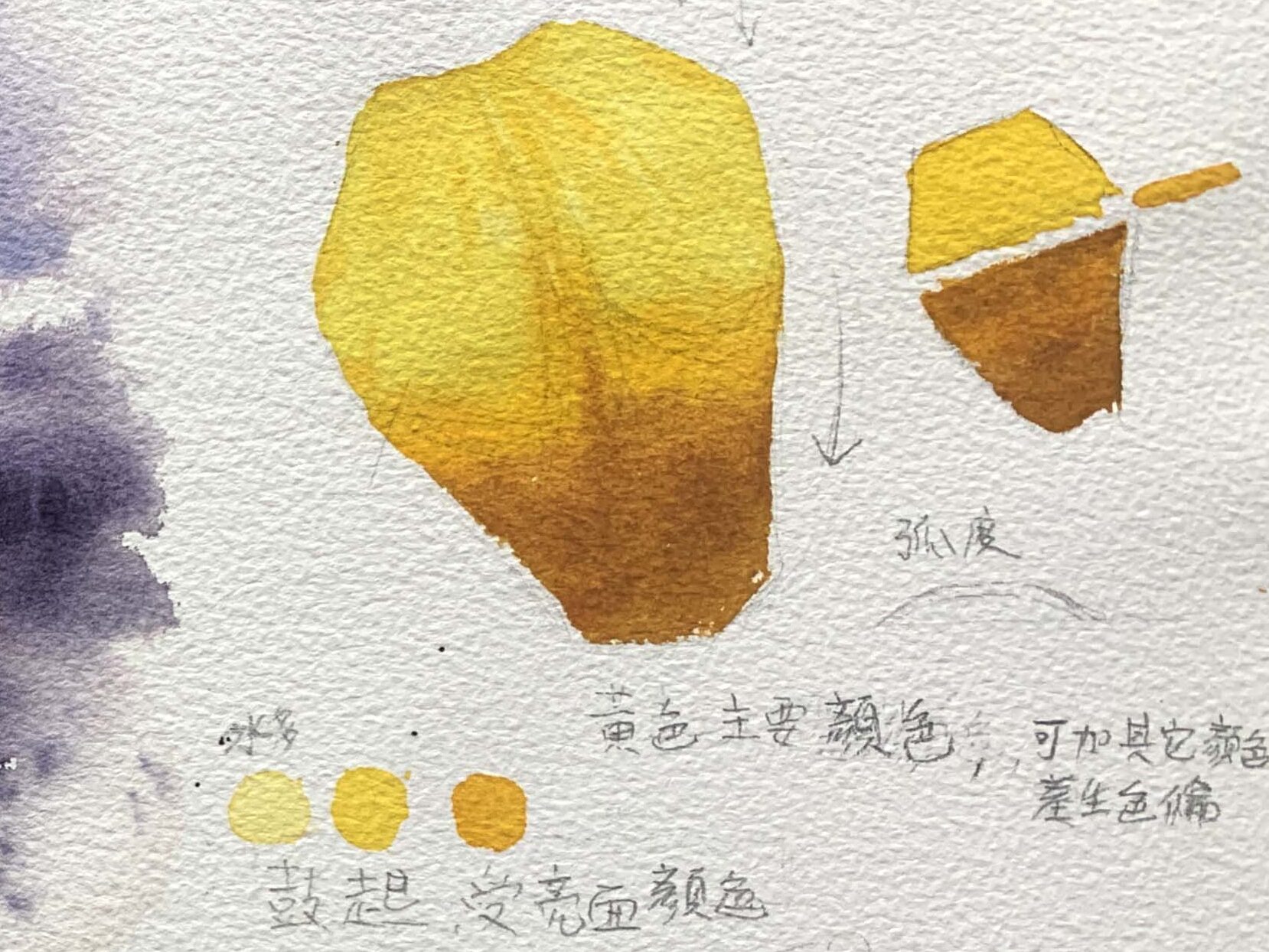


Highlights (Areas Exposed to Light)
Use bright colors (e.g., cadmium yellow or lemon yellow for yellow lilies, diluted cadmium red or pink for red lilies).
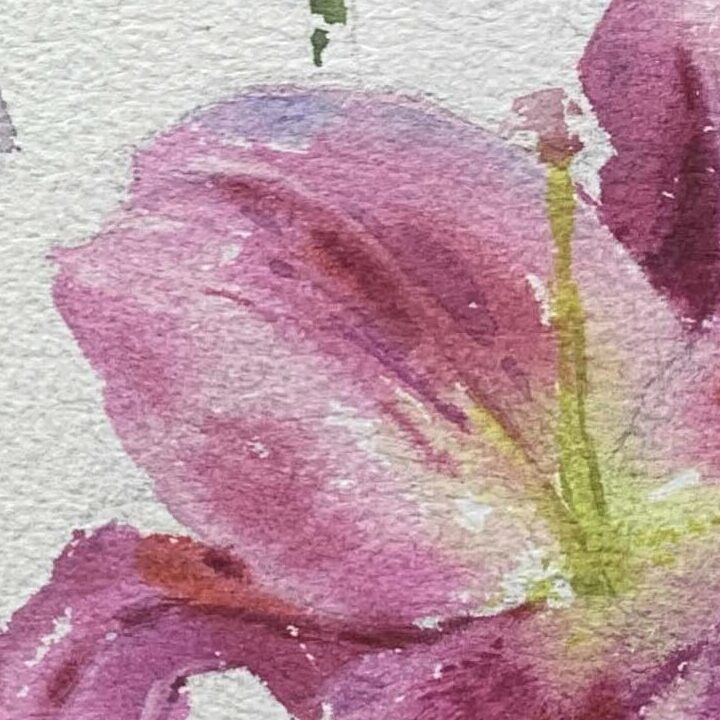
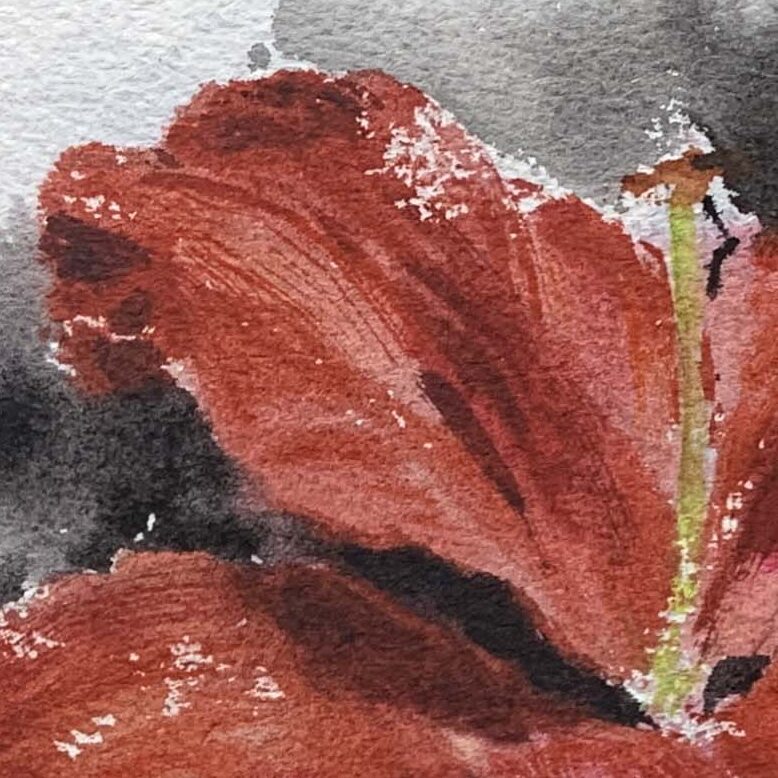
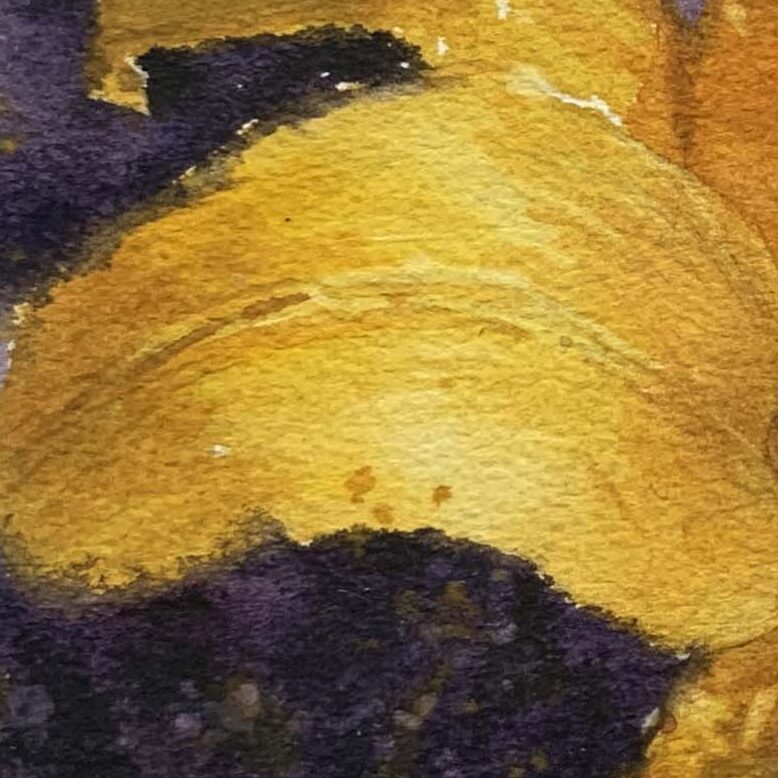


Midtones (Transition Areas)
Lower the saturation slightly to create a natural transition (e.g., mix a bit of orange, red, and yellow to form orange-leaning yellow or orange-leaning red).
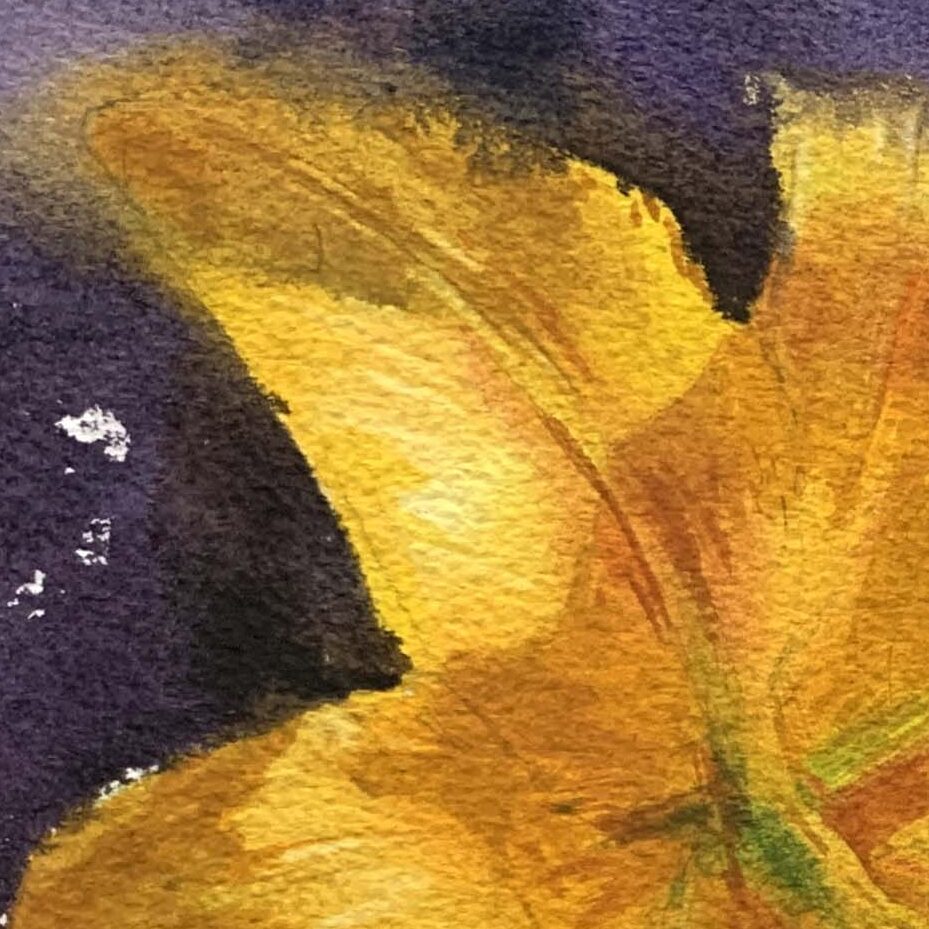

Shadows (Dark Areas)
Use complementary or cool colors to depict the color variations caused by surface folds. For red lilies, shadows can be achieved using cerulean blue mixed with alizarin crimson or ivory black.
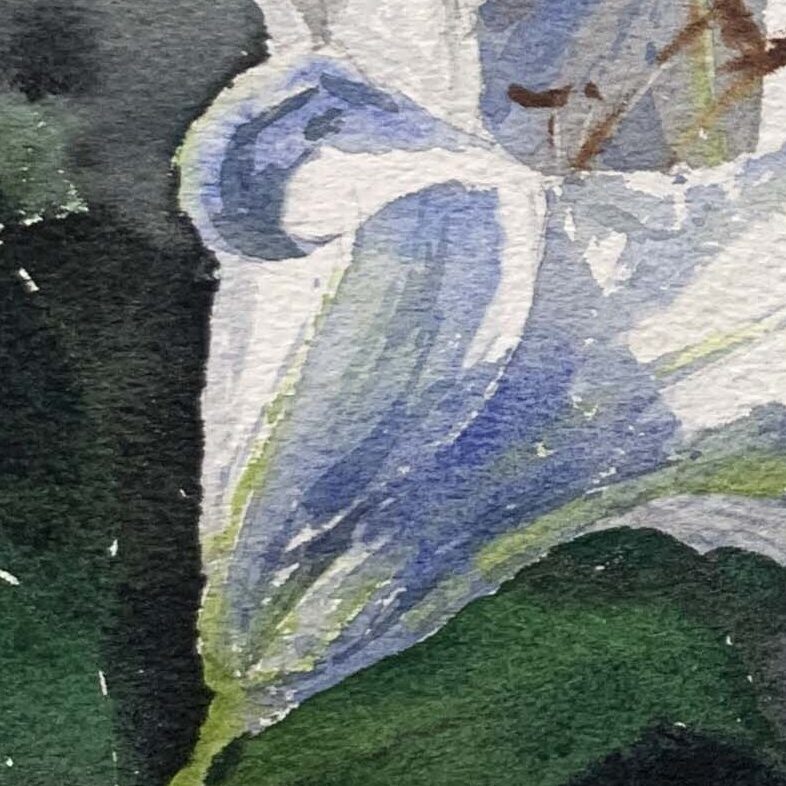
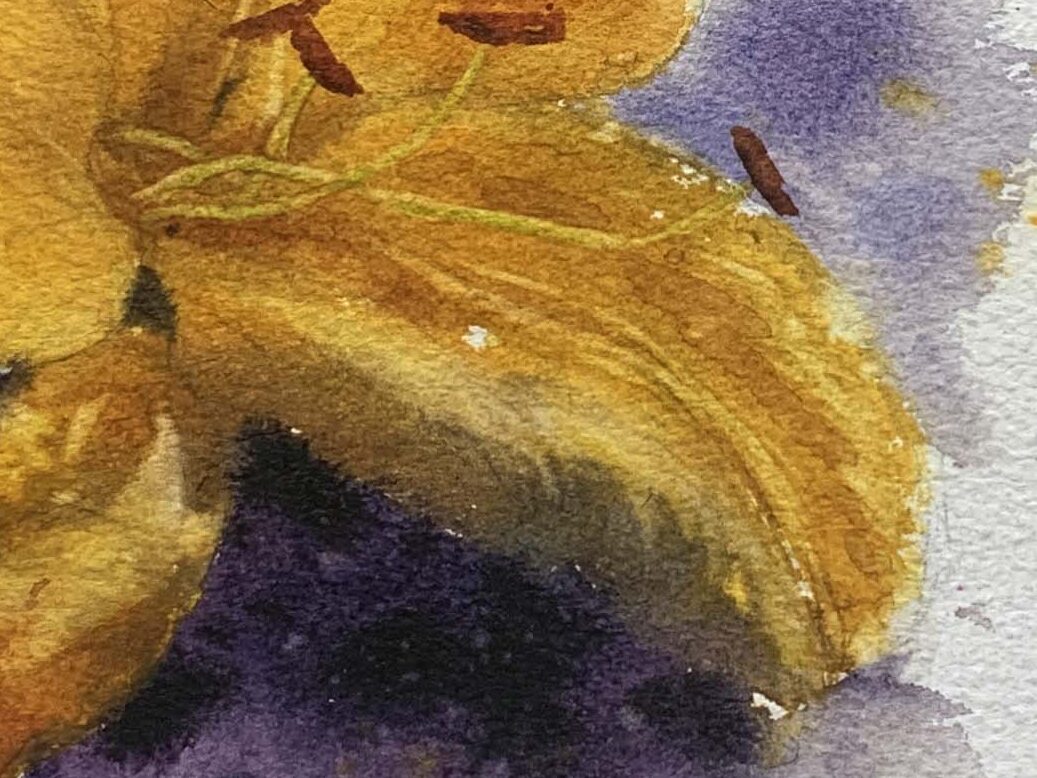
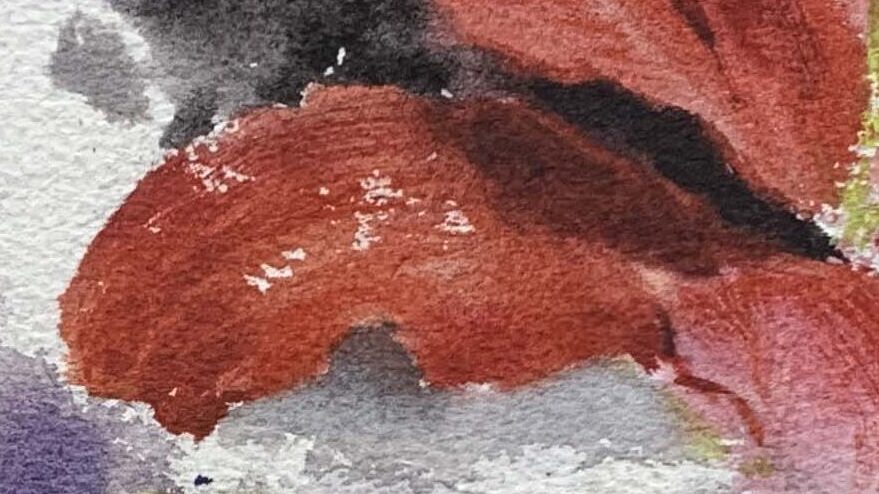




Petal Texture and Detail Handling
1. How to Achieve Softness in Petals
Petals are typically semi-transparent, and to create a soft transition, it's essential to keep the brightness (lightness and darkness) variations subtle while layering colors on a wet surface.

To enhance the richness of petals, observe the length and shape of the petal edges and create variations between blurred and sharp edges.
If you want to understand the principles of color value and saturation, as well as their application methods, please click on this introductory article on color mixing that I wrote.
2. How to Render Petal Details
When the petal is semi-dry and almost dry, apply deeper colors in small dabs, or wait until it’s completely dry before layering thin washes to depict petal textures.


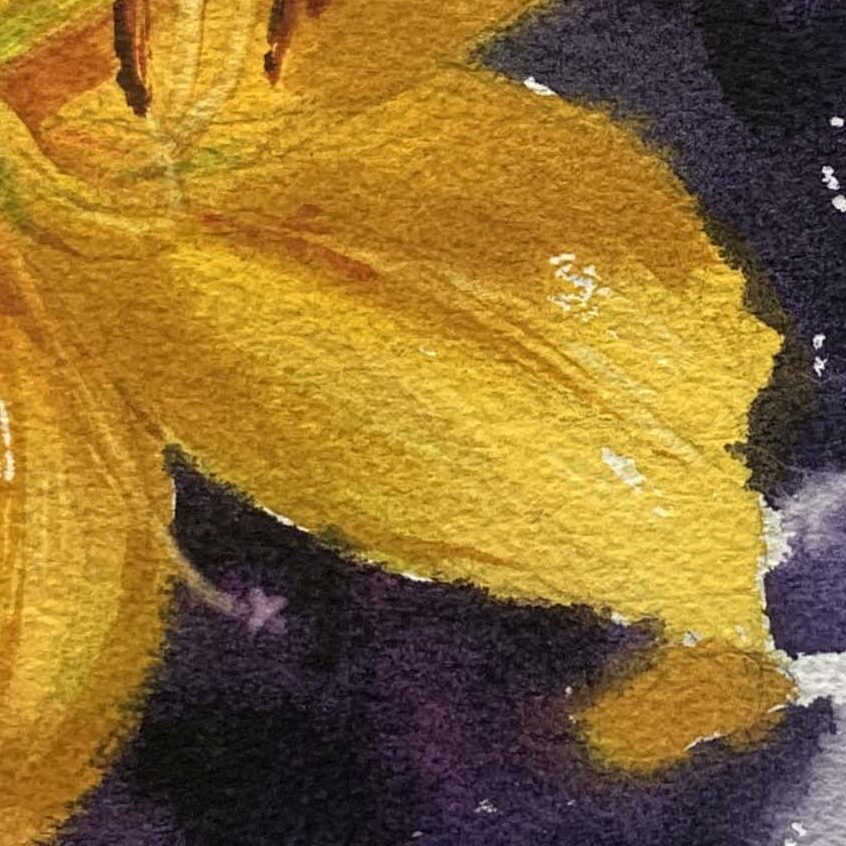
Background Treatment and Color Matching
A dark background enhances the visibility of white or light-colored flowers, making them stand out. A light or even background-free approach is suitable for lilies with mid-gray brightness, allowing more focus on rendering the petal folds.
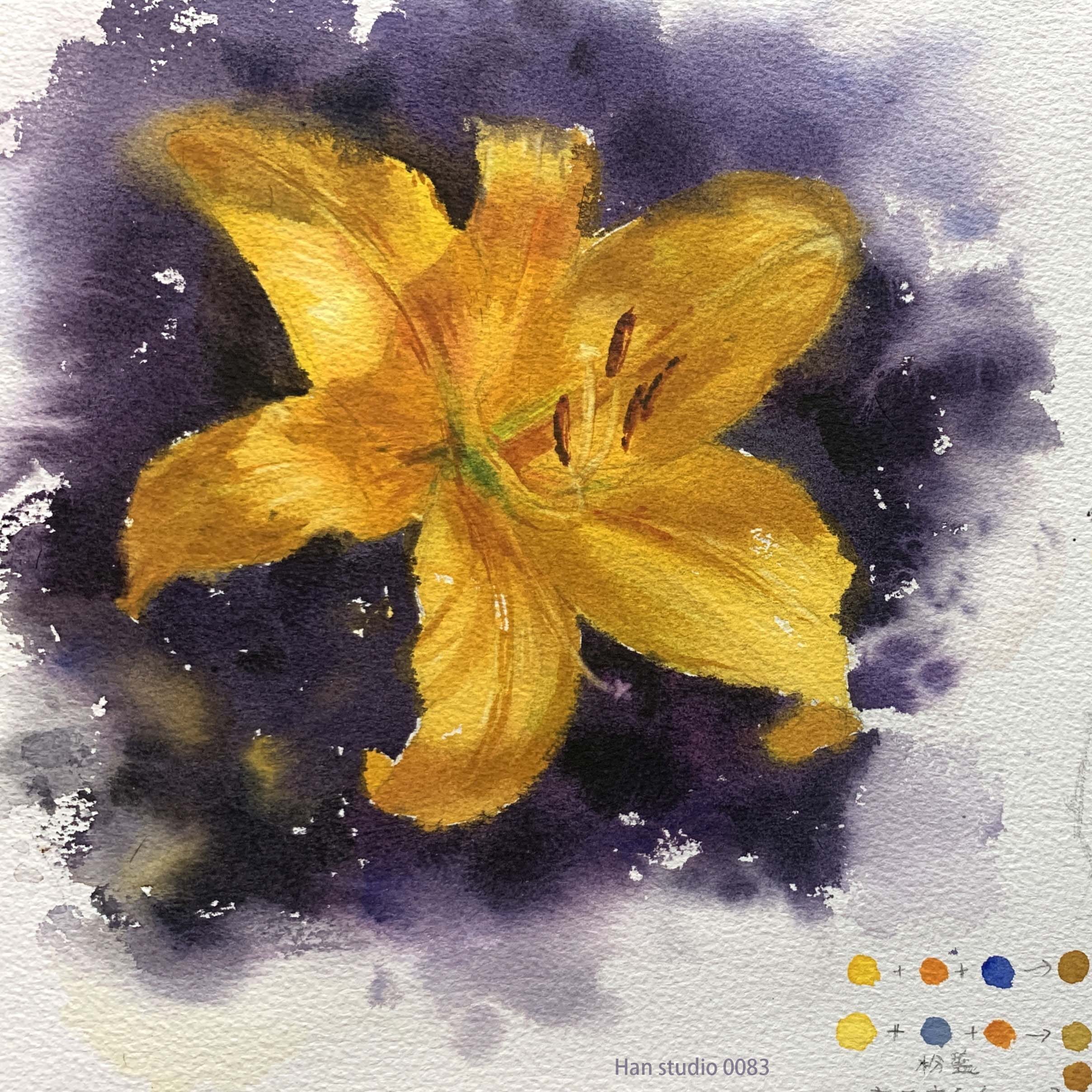


Color Mixing and Matching Tips
How to Choose Colors?
Lilies come in various colors, such as white, yellow, pink, red, and orange, but you can also modify the colors subjectively.

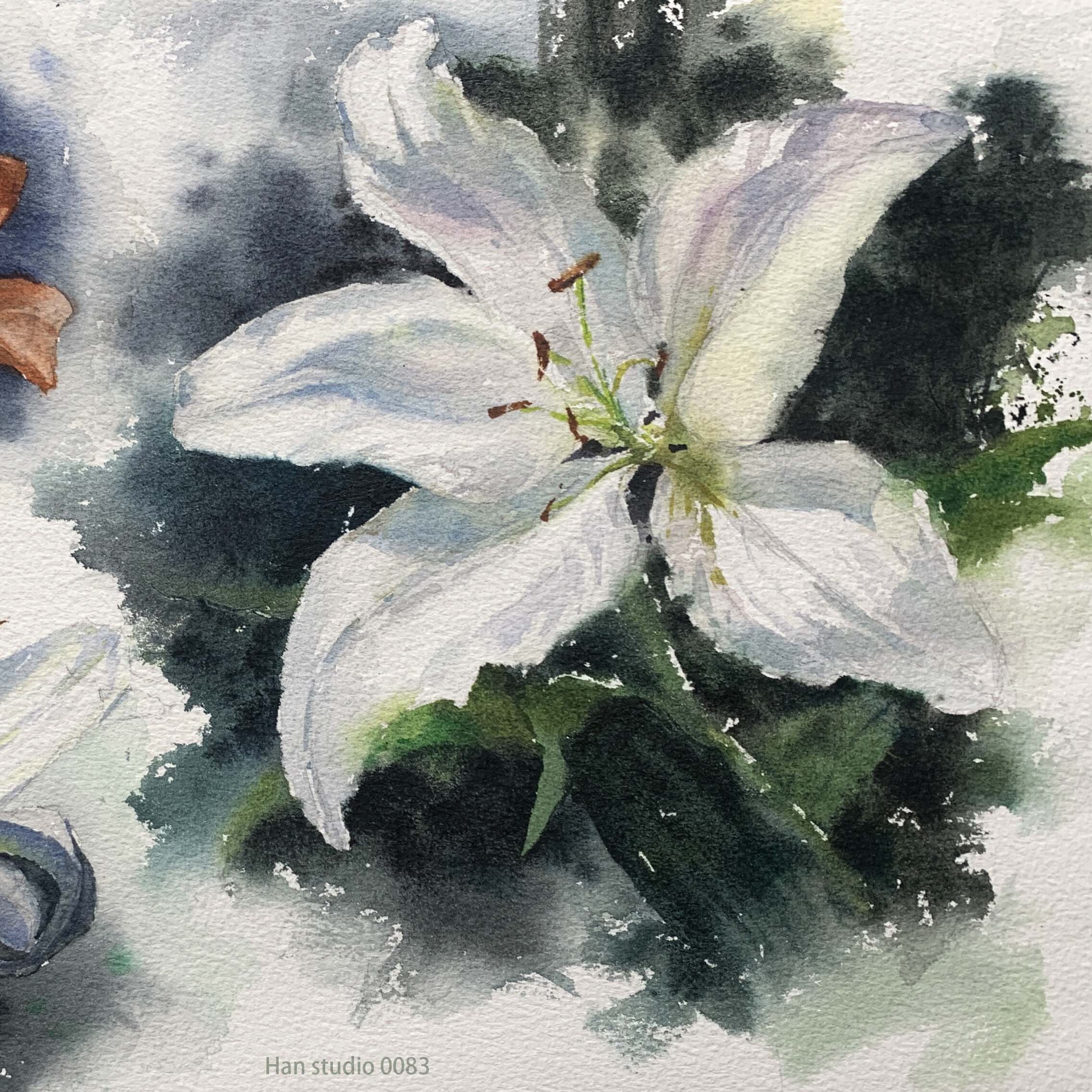
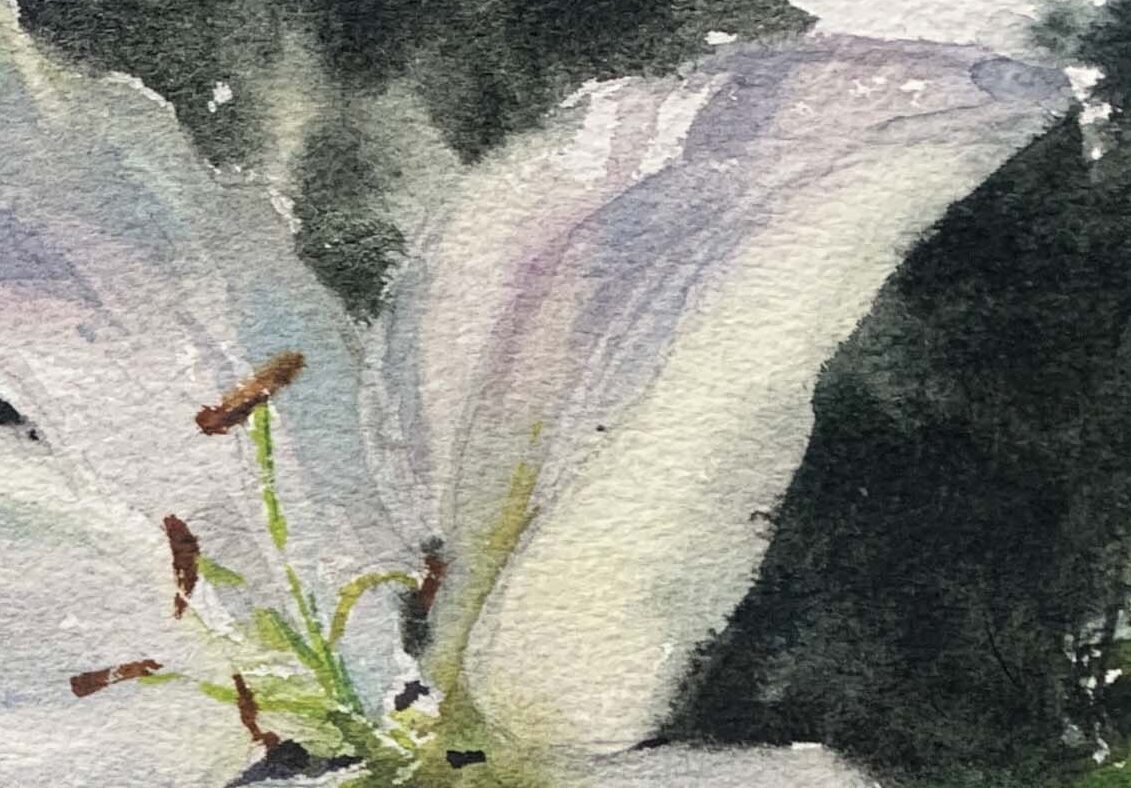
White Lilies: Observing real flowers, you’ll notice that shadow areas can include cool and warm hues (e.g., bluish-purple or grayish-purple) to create depth.

Yellow Lilies: Primarily warm-toned (lemon yellow (greenish-yellow), cadmium yellow (slightly reddish-yellow), deep yellow, and orange-red). Shadows can include a small amount of blue to create a more muted yellow.

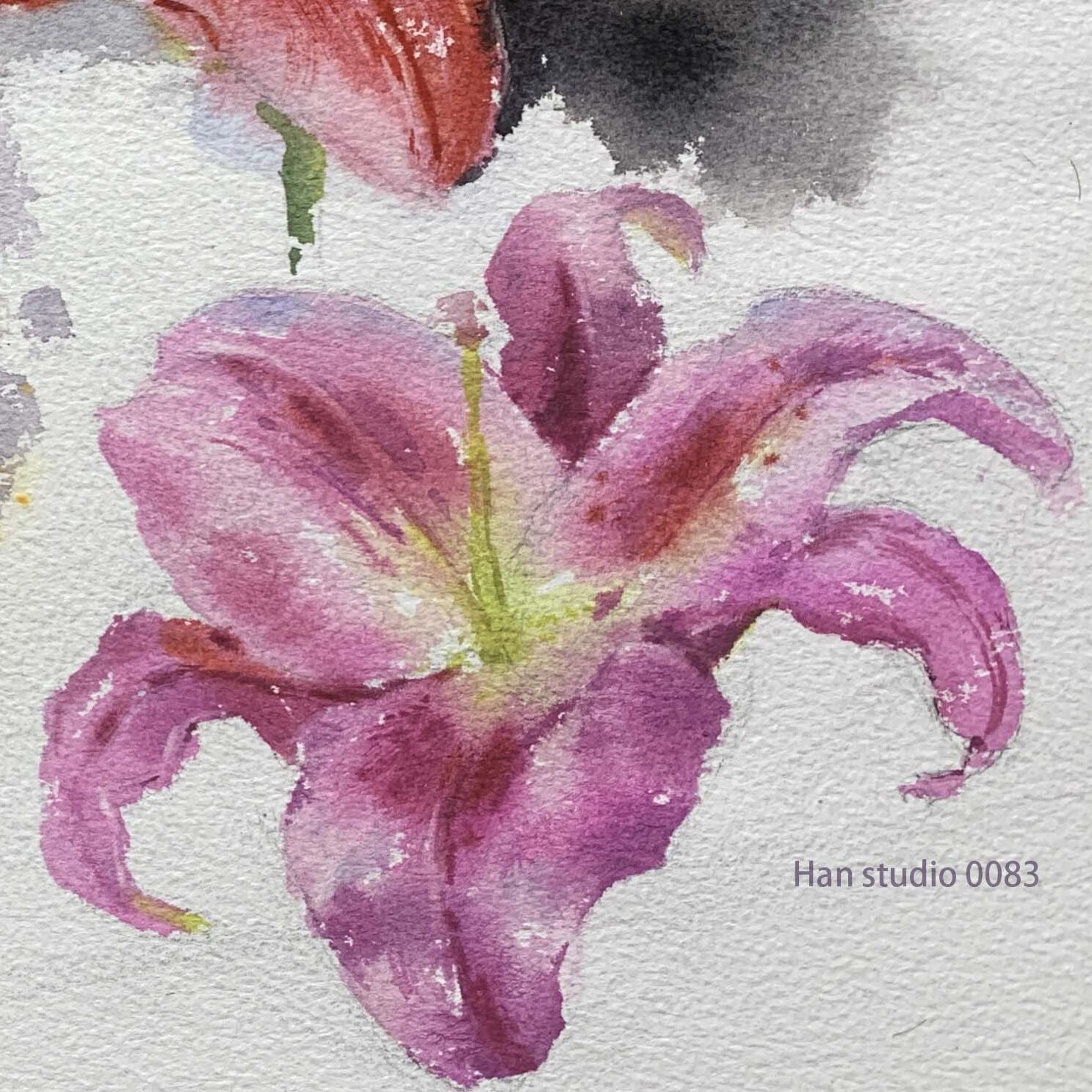
Pink and Red Lilies: For light pink petals, dilute cadmium red with water, or mix pink-beige and pink-blue with cadmium red.
For deeper shades, mix alizarin crimson, cerulean blue, or other purplish-reds.

How to Match Colors in Different Areas?
Light and Shadow Influence:: Different areas of the petals will be affected by light, so use warm and cool colors to create depth.
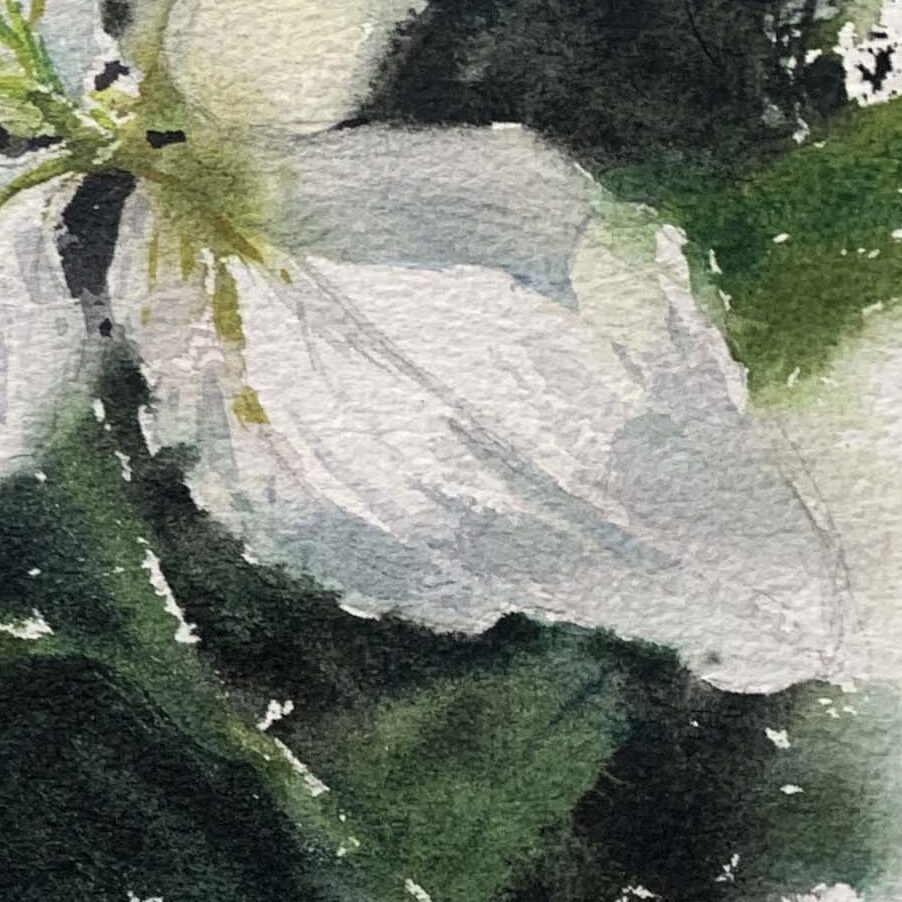

Reflective Colors:Flowers and their surroundings interact, meaning petal edges might reflect background hues. For example, green leaves might influence the petal color.
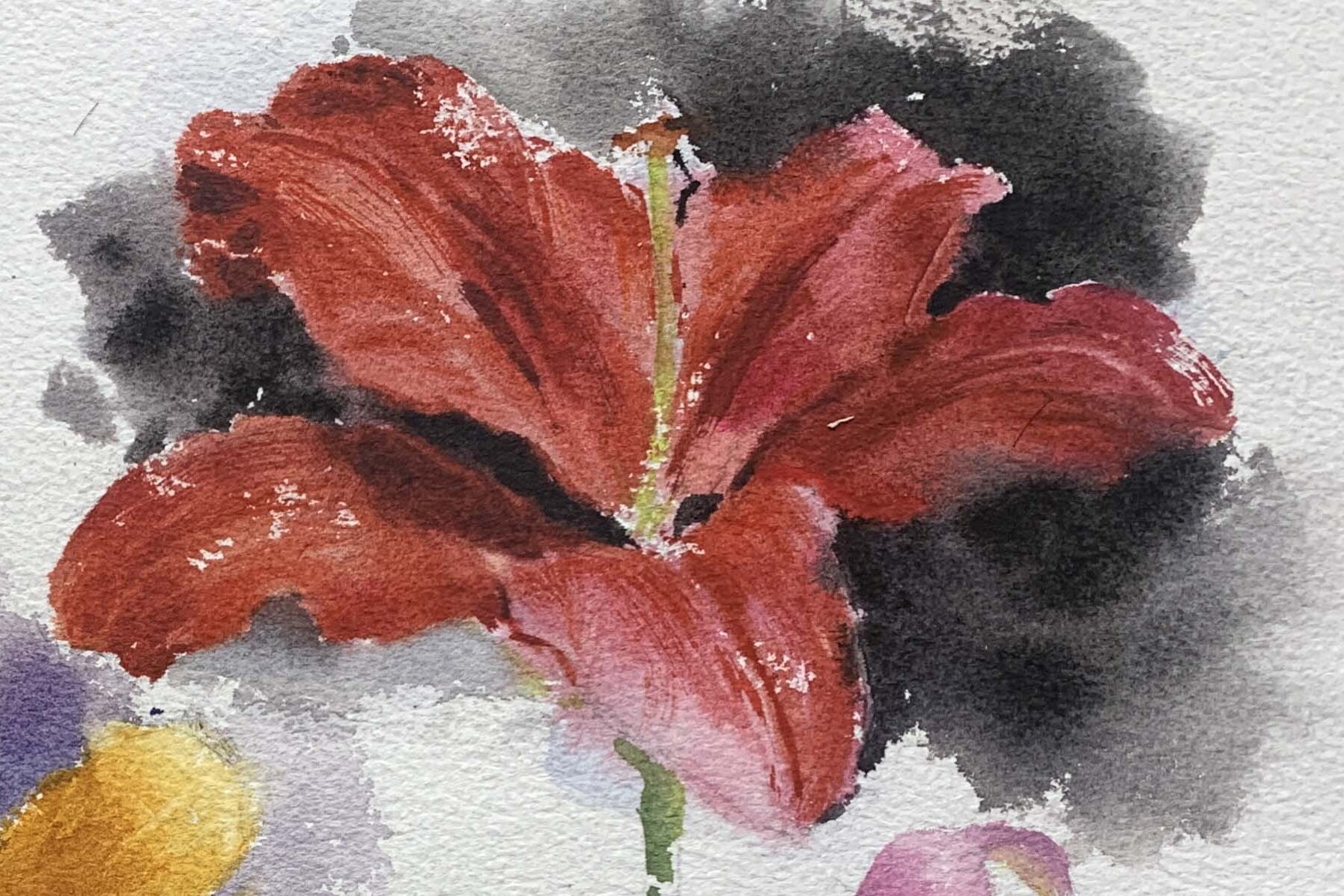

Floral Painting Practice Suggestions
- Try blending the background with the flower while the paint is wet, allowing the colors to merge naturally and interact.
- Focus on distinguishing between clear and blurred petal edges. Choose a background contrast that enhances the flower's presence in the composition.
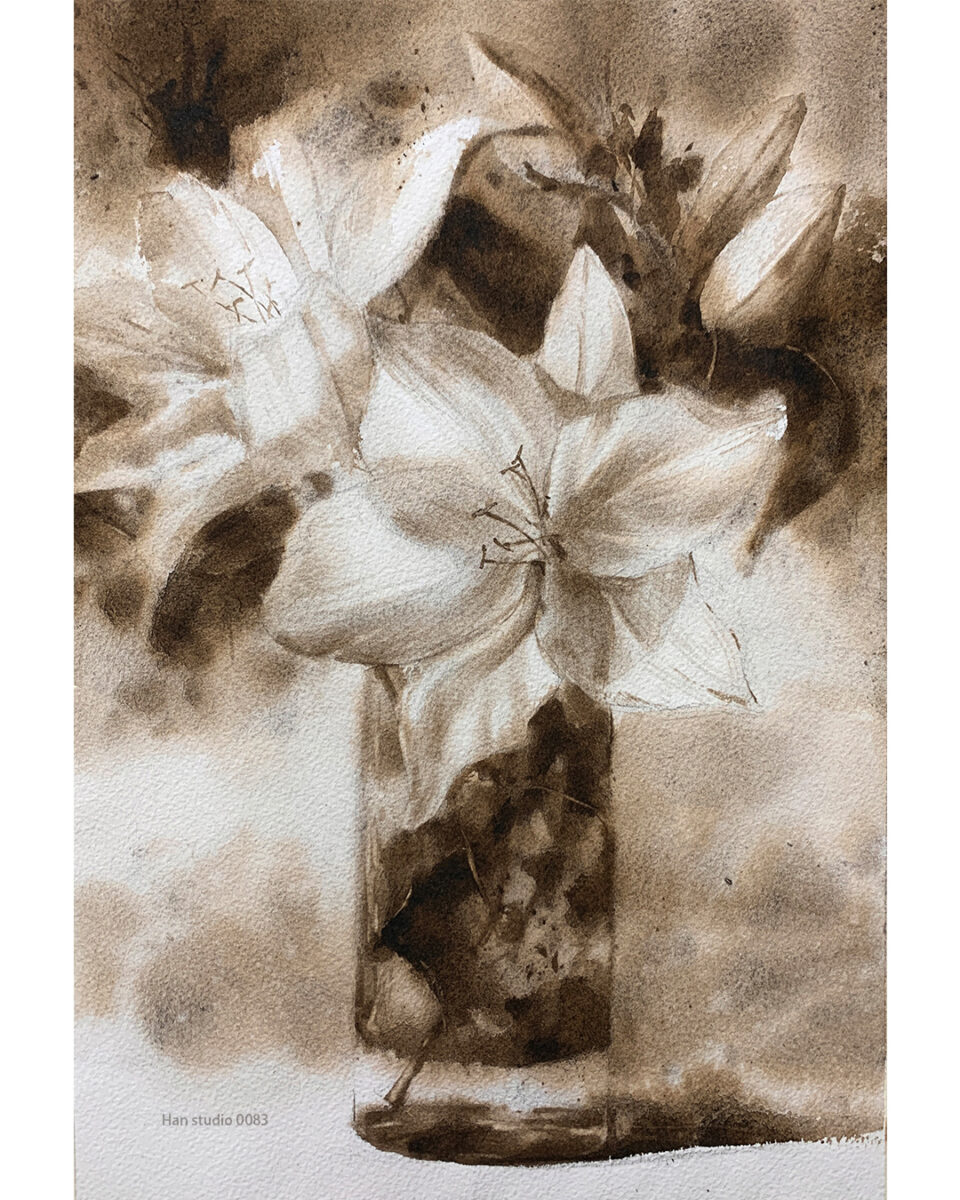

This guide covers watercolor techniques for painting flowers. Have you encountered difficulties with color mixing or other aspects while painting flowers?
If you're interested in learning to draw but don't know where to start, or if you'd like to understand the knowledge behind drawing,
feel free to join my LINE and contact me. In my classes, I organize drawing methods in a clear and structured way.
Click here to learn more about my drawing courses!
Want to explore more articles on extended drawing techniques?
- Watercolor Topics
Watercolor Mixing Tips: Achieve Natural Transitions Easily
How to Watercolor Grapes: Master Light, Shadow & Gradients
How to Paint the Light and Dark Layers of a Monstera Leaf
How to Paint a Vibrant Yellow Bell Pepper Still Life
How to Paint a Luminous Banana with Watercolors
- Still Life Topics
How to Draw a Car for Beginners: Using Simple Shapes
How to Draw Perspective: Basic to Complex Structures
Boots Sketch Tutorial: Learn Proportions and Structural Lines
How to Master the Proportions,Shape, and Symmetry of a Teapot
Three Easy Steps to Drawing a Stuffed Duck with a Pencil
Sketching Class Fishing Boat Drawing Techniques
- Portrait Topics
How to Draw Arms: Learn Arm Movements and Bone Proportions
Human Skull Sketch: Learn Anatomy for Accurate Portraits
How to Accurately Master Hand Proportions and Joint Structure
How to Draw Ears:Simplified Ear Structure and Shading Tips
How to Use Two-Tone Shading: Simple Shadow Techniques
How to Sketch Facial Muscles: Capture Realism and Expression
How to Draw Masks: Use Perspective and Shadows
Building Up from Simple Contours to Detailed Eye Portraits
Capturing Realism in Lip Drawing: Key Structures and Shading
Understanding the Three Key Elements of Head Structure
Mastering the basic proportions and structure of portrait drawing

Leave a Reply